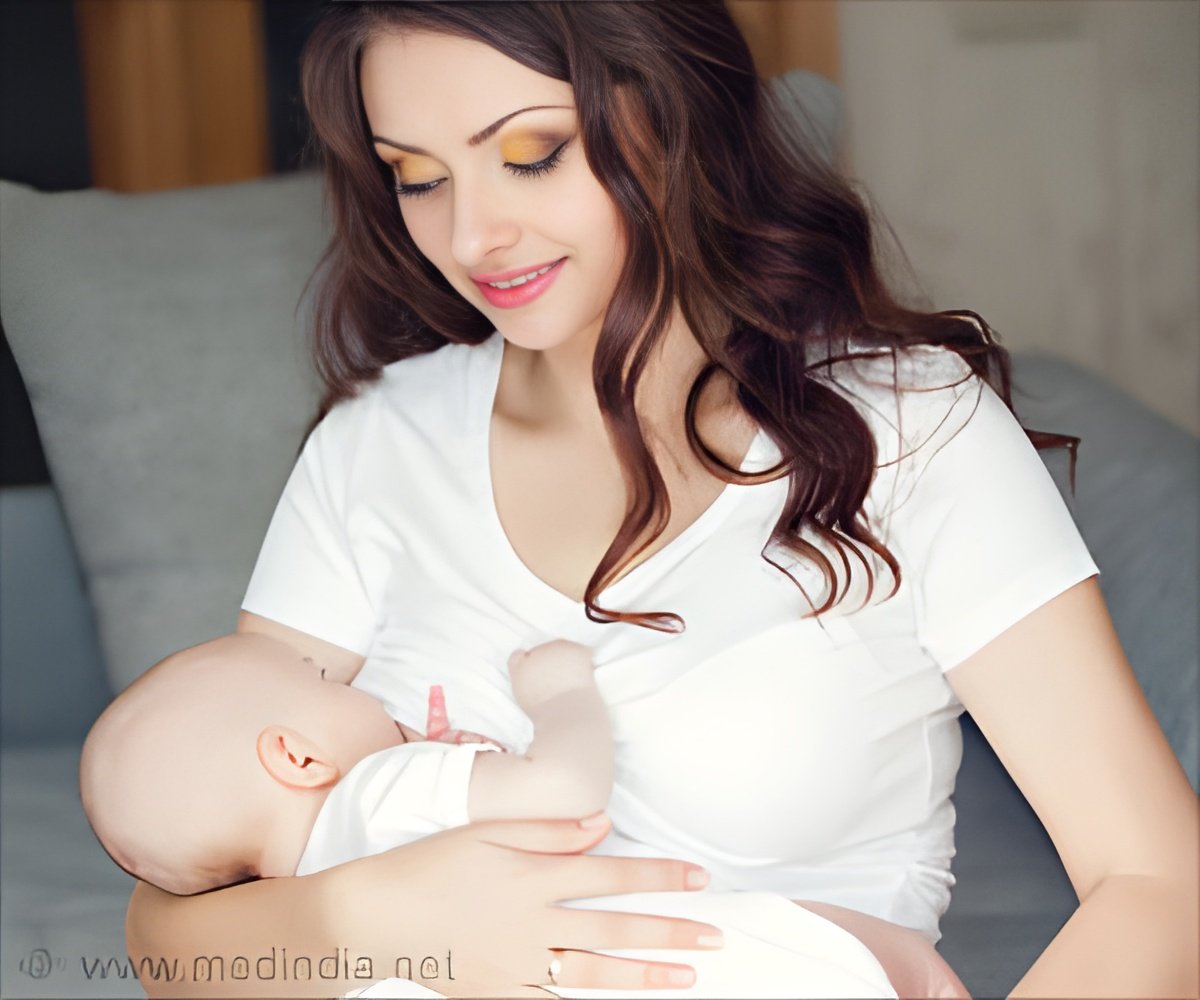
There is need for more public health strategies that directly inform women and girls about the maternal and fetal benefits of breastfeeding.

TOP INSIGHT
Hormone-receptor-negative (HRN) breast cancers are more serious as they are diagnosed at later stages, respond to fewer treatment options and are less likely to be cured by current therapies. A new study revealed the long-term protection of breastfeeding against the most aggressive subtypes of breast cancer to be very encouraging.
Weiss said, "Further evidence to support the long-term protection of breastfeeding against the most aggressive subtypes of breast cancer is very encouraging and actionable."
These findings highlight the need for more public health strategies that directly inform women and girls about the maternal (and fetal) benefits of breastfeeding before and during a woman's child-bearing years. The researchers said, "It is also important for these women to have the message reinforced by their healthcare professionals."
The study findings suggest that it is critical to remove the barriers to breastfeeding at home, in the community and in the workplace.
The study was published in Annals of Oncology.
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA


 Email
Email










