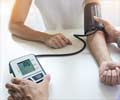
Low blood pressure during surgery puts patients at higher risk for postoperative delirium. Postoperative delirium, a change in mental function that can cause confusion after surgery
TOP INSIGHT
Postoperative delirium, a change in mental function that can cause confusion after surgery and the most common surgical complication for older adults, can be caused by a wide variety of factors, including pain, stress, insomnia and anxiety.
In the study of 316,717 patients who had non-cardiac surgery at one of two hospitals between 2005 and 2017, 2,183 (0.7%) were diagnosed with delirium within 30 days after surgery. Of those patients, 41.7% a had mean arterial pressure (an average of systolic and diastolic blood pressure) below 55 mmHg during surgery for fewer than 15 minutes and 2.6% had it for longer than 15 minutes. The researchers, including lead authors Luca J. Wachtendorf, B.S., and Omid Azimaraghi, M.D., found that patients who experienced low blood pressure were up to 60% more likely to experience postoperative delirium, and the effect was magnified in patients who had longer surgeries.
While postoperative delirium can affect anyone, elderly patients are at highest risk. Postoperative delirium typically lasts one to three days after surgery, although some patients experience long-term memory loss and difficulty learning, concentrating and thinking.
“Physician anesthesiologists measure patients’ blood pressure at least every three minutes during surgery,” said Dr. Eikermann. “The study shows they can help decrease the risk of postoperative delirium by immediately providing medication to increase blood pressure when it falls.”
Source-Eurekalert
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA

 Email
Email