A new, unexpected mechanism whereby genes from bacteriophages enable bacteria to use their hidden potential and establish a new function.
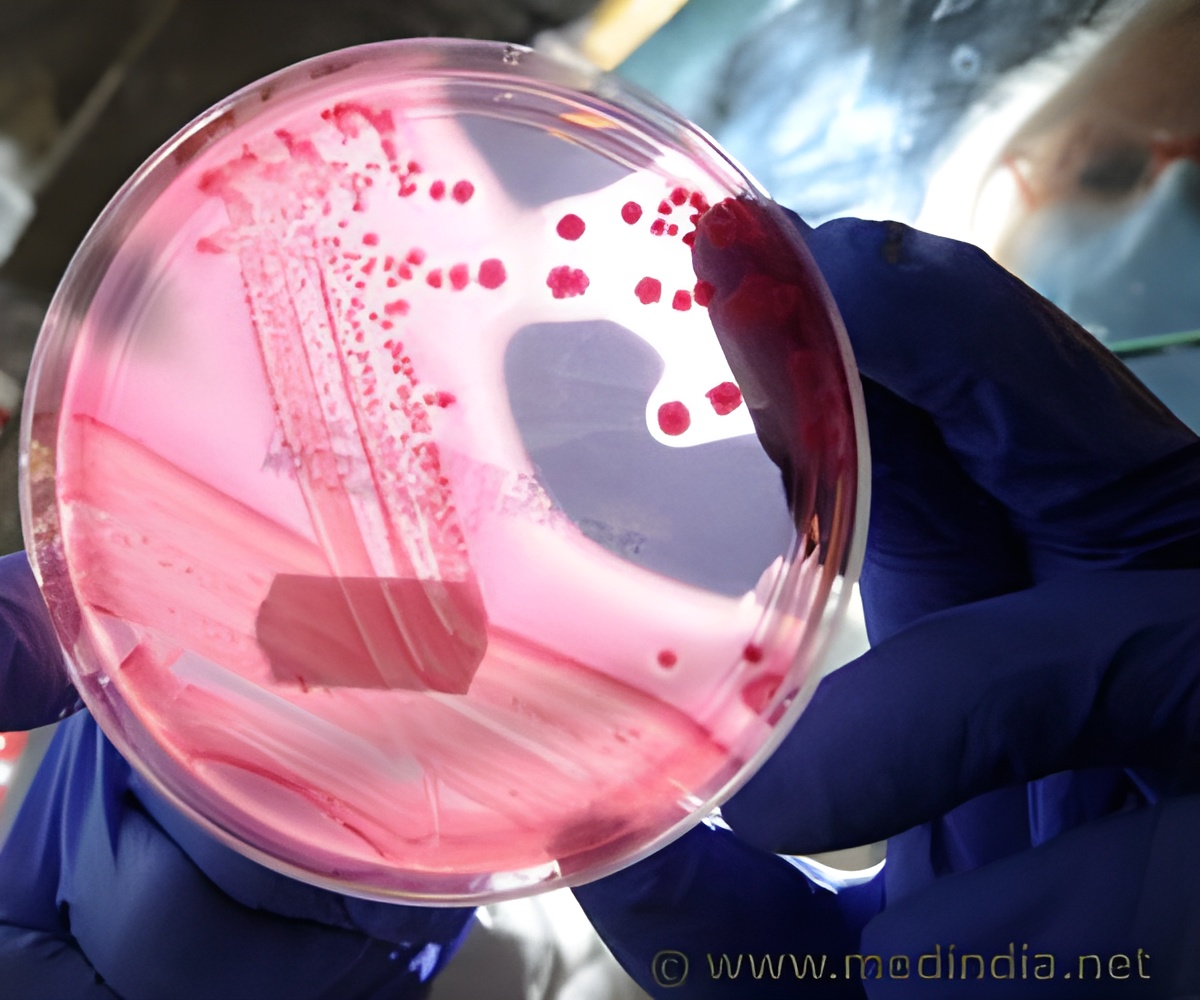
New study revealed how bacteriophages, instead of killing bacteria, transmit genes that help the bacterium Escherichia coli (E. coli) survive. The study was published in Nature Ecology & Evolution.
Bacteriophages are the most numerous organisms on Earth (about 1031). Every day, they infect and kill 15-30 % of all bacteria in the world's oceans. "We found a new, unexpected mechanism whereby genes from bacteriophages enable bacteria to use their hidden potential and establish a new function," says researcher and lead author Jon Jerlström-Hultqvist.
TOP INSIGHT
Bacteriophages (viruses that infect bacteria) contribute to new functions by revealing hidden potential in their bacterial hosts.
First, the scientists removed an essential gene (ilvA) from the bacterium. They then investigated whether bacteriophage genes (isolated from Svandammen, "Swan Pond", in central Uppsala) could rescue the bacteria. The researchers identified a new group of genes that code for enzymes: S-adenosyl methionine (SAM) hydrolases. These enzymes break down SAM and, as a result, boost biosynthesis of the amino acid methionine, a precursor to SAM. One of the enzymes required for methionine biosynthesis has a side reaction that enables the E. coli bacterium to compensate for the absence of the essential ilvA gene.
The study in question shows that, to understand how a bacterium works, the functions normally found in bacteria are not the only ones that need investigating. The hidden potential of the bacterial cell can be manifested when its metabolic state changes, for example in a bacteriophage infection. According to Professor Dan I. Andersson, who heads the study in question,
"The new function in this study is that these bacteriophage enzymes have the ability to break down an important cell component (SAM) of the bacterium. When this component breaks down, the bacterial cell resets its metabolism and a new function becomes available. Moreover, it is very important to understand the hidden potential of bacteria and whether it can affect the development of antibiotic resistance and its pathogenicity," says Professor Andersson, who heads the study.
Source-Eurekalert
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA

 Email
Email







