- Fetal Echocardiogram Test - (http://www.heart.org/heartorg/conditions/congenitalheartdefects/symptomsdiagnosisofcongenitalheartdefects/fetal-echocardiogram-test_ucm_315654_article.jsp#)
- Ultrasound of Fetal Cardiac Anomalies - (http://www.ajronline.org/doi/full/10.2214/ajr.10.7287)
- Fetal echocardiography - (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/fetal_echocardiography)
What is Fetal Heart Ultrasound?
Fetal echocardiography helps in diagnosis of cardiac birth defects, and is similar to the ultrasound procedure during pregnancy. Also known as fetal heart ultrasound or fetal echo, it is used to view your unborn baby’s heart, assess fetal heart circulation, flow of blood in the various chambers of heart and fetal heartbeat.
Among the various types of ultrasound during pregnancy, the fetal ultrasound done during the first trimester is to confirm the pregnancy and its course.
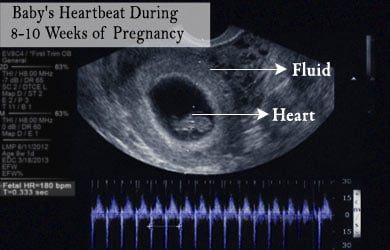
Fetal echocardiography is typically performed during the second trimester of pregnancy, at about 18 to 24 weeks of pregnancy. Sound waves are sent through the abdominal skin that bounce off the fetal heart surfaces and produce an echo. This echo is recorded by the machine to create an image called echocardiogram. Such a sonogram image of the fetal heart can give a lot of information about the structure, function and blood flow of the heart. Abnormalities in the size, shape and closure of heart valves can be detected in the fetal ultrasound.
Fetal heart defects ultrasound procedure can be performed in two ways.
Abdominal: Abdominal ultrasound scan is the more common way of fetal echocardiography. A gel is applied on the abdomen of the mother and a transducer or probe is used to send sound waves from the surface of the abdomen.
Transvaginal Ultrasound: A small transducer is inserted into the vagina with the help of a catheter. The transducer rests at the back of the vagina from where the pictures of the fetal heart can be taken.
Indications of Fetal Echocardiography
Fetal echocardiography is prescribed to a pregnant woman if there are any risk factors or possibilities of heart disease of the unborn child. Some of the risk factors that indicate a fetal heart ultrasound procedure include:
- Any abnormality in the fetal heartbeat detected at the time of ultrasound procedure done during pregnancy
- Family history of heart disease
- Previous child with a congenital heart disease
- The pregnant woman has had medical conditions such as rubella, Parvovirus, Coxsackie, type 1 diabetes, lupus or phenylketonuria
- Intake of any medications prescribed for epilepsy or prescription acne drugs during pregnancy
- Use of drugs or alcohol during pregnancy
- Autoimmune Disease, Anti Rho/La positive

Any abnormalities noticed during the ultrasound scans in the first trimester of pregnancy can be indicative of a detailed fetal echocardiogram.
- Increased nuchal fold thickness: More than 3 mm in thickness
- Abnormal ductus venosus
- Any chromosomal abnormality
- Fetal dysrhythmia (abnormal heart rate)
- Hydrops (Excessive accumulation of serous fluid in tissues of cavities of the body)
- Extracardiac abnormality noticed in screening ultrasound
Who does the Fetal Echocardiogram Procedure?
The procedure of ultrasound is done by an experienced ultrasound technician, called an Ultrasonographer, or the consultant obstetrician. The results of the ultrasound examination will be then reviewed by pediatric cardiologist for diagnosis, prognosis and determining the course of action.
Unlike some of the ultrasound procedures, this procedure does call for a full bladder. The procedure can take from about 30 minutes to 2 hours, depending on the position of the fetus in the womb, clarity of the ultrasound and the details required by the obstetrician.
It is advisable to bring any medical records for the information regarding any previous treatments undertaken.
Viewing the Fetal Heart with Ultrasound
The first step to fetal heart screening is to define the side of the heart, based on the position of the fetus inside the womb. After this, the heart is viewed from various angles. But when it comes to interpreting the sonogram image, it should be used to visualize the fetus from inferior to superior.
Four transverse images of the fetus are obtained for readings and detecting any possible abnormality of the fetal heart.
- Abdominal transverse image: The stomach is located on the left side, in front of the fetal spine. The positions of the descending aorta and the superior vena cava are confirmed. Any abnormalities in the position of the heart, called cadiac situs, can be identified.
- Four-chamber view: The ultrasound beam is directed perpendicular to the chest of the fetus and the four chambers of the heart are identified. The atrioventricular valves can be viewed with real time opening and closing of the valves during systole and diastole. The pulmonary venous and its connections can also be checked. The four-chamber view of the fetal heart helps identify abnormalities like ventricular and atrial septal defects, tetralogy of Fallot, coarctation of aorta, and size of the atria and the ventricles.
- Three-vessel view: In this view, the pulmonary artery (arising from the right ventricle), cross-section of ascending aorta and the superior vena cava can be seen. The three great blood vessels need to be in line with each other. The aorta and pulmonary artery must be perpendicular to each other. Heart defects such as transposition of arteries can be identified during the three-vessel view.
- Three-vessel and Trachea view: The positions of the three vessels with respect to trachea can be seen.
- Doppler technique: The fetal heart Doppler method measures the fetal blood flow in different parts of the baby’s body including umbilical cord, brain and heart. The method helps to measure the adequacy of oxygen and nutrient supply to the fetus via placenta. Blood flow in the uterine artery and the umbilical artery. Cardiotocograph is a form of Doppler that uses only sound, without producing images, and monitors the heartbeat rate and rhythm of the fetal heart.
Abnormalities detected in a Fetal Echocardiography
Fetal heart abnormalities detected through ultrasound include structural congenital heart disease that can be diagnosed in the uterus using the fetal echocardiogram.
Hypoplastic left heart syndrome: A rare congenital defect in which the left ventricle of the heart is underdeveloped. The aortic and mitral valves are also too small to allow sufficient blood. The condition is usually accompanied by an atrial septal defect.
Truncus arteriosus: This is a rare congenital heart defect in which only one large blood vessel leads out of the heart, instead of two separate blood vessels to carry deoxygenated blood to the lungs and oxygen-rich blood to the other parts of the body. Further, the wall that divides the right atrium from the left is missing in this condition. This mixes up the deoxygenated and oxygen-rich blood. This condition needs to be treated surgically before the baby is 2 months old.
Transposition of great vessels: The condition is a collective term for a group of congenital heart defects that occur in combination. There is an abnormal spatial arrangement of the great vessels, namely superior vena cava and/or inferior vena cava, pulmonary artery, pulmonary veins and aorta.
Transposition of great arteries: This condition refers to the abnormal positioning or interchanged position of the pulmonary artery and aorta only.
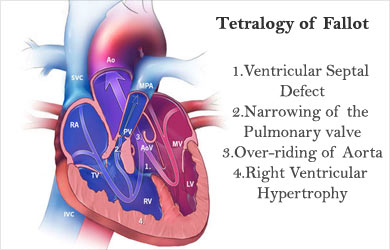
Tetralogy of fallot: A typical combination of four anatomical abnormalities of the heart is called tetralogy of Fallot. It is the most common congenital heart defect. The four conditions include:
- Narrowing of the pulmonary valve
- Ventricular septal defect
- Over-riding of aorta
- Right ventricular hypertrophy
Ventricular and Atrial Septal defects: Septum is the wall that separates two atria and two ventricles from each other. Any hole in this wall is called septal defect. If the hole is between two atria, it is atrial septal defect and if it is located between two ventricles, it is called ventricular septal defect.
Doppler Fetal Echocardiography
Fetal ultrasound usually done is a detailed analysis of the sonogram images obtained from two-dimensional ultrasound procedure. A Doppler can be performed with the same instrument used in the ultrasound procedure, if it has the Doppler function.
Doppler sonography measures the blood flow to the different parts of the body of the fetus. It is usually performed during the third trimester. The indications for a Doppler ultrasound include:
- Inadequate amniotic fluid
- Rh-incompatibility
- Twins sharing the same placenta
- Inadequate growth of the fetus
Doppler scans are done to assess blood flow in the uterine artery and umbilical artery. Cardiotocograph is a type of Doppler that uses only sound as output without producing an image. It helps in monitoring the fetal heartbeat.
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA
 Email
Email




