- Hornibrook J. A balance test for chronic perilymph fistula. Int J Otolaryngol. 2012;Article ID 163691, 8 pages.
- Hornibrook J. Perilymph fistula: fifty years of controversy. ISRN Otolaryngol. 2012;2012:281248. - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3658483/)
- Ikezono T et al. The diagnostic performance of a novel ELISA for human CTP (Cochlin-tomoprotein) to detect perilymph leakage. PLOS One. 2018; 13(1):e0191498 - (https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article/file?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0191498&type=printable)
- Minor LB. Labyrinthine fistulae: pathobiology and management. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2003;11(5):340-346 - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14502064)
- Hornibrook J. The postural and cognitive disabilities of chronic perilymph fistula (PLF) after mild head trauma. Ann Clin Case Rep.2018;3:1514. - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3658483/)
- UCI health. Perilymphatic fistula - (http://www.ucihealth.org/medical-services/ear-nose-throat-ent/hearing-ear-disorders/perilymphatic-fistula)
- Bhatia N, Lehrer JF. Perilymphatic fistula: an approach to diagnosis and management that provides surer diagnosis and provides medical and surgical management options: report of six illustrative recent cases. Int Tinnitus J. 2012;17(1):61-66. - (http://www.ucihealth.org/medical-services/ear-nose-throat-ent/hearing-ear-disorders/perilymphatic-fistula)
- Al Felasi M et al. Perilymphatic fistula of the round window. Eur Ann Otolaryngol, Head and Neck Dis. 2011;128(3):139-141. - (http://www.ucihealth.org/medical-services/ear-nose-throat-ent/hearing-ear-disorders/perilymphatic-fistula)
What is Perilymph Fistula?
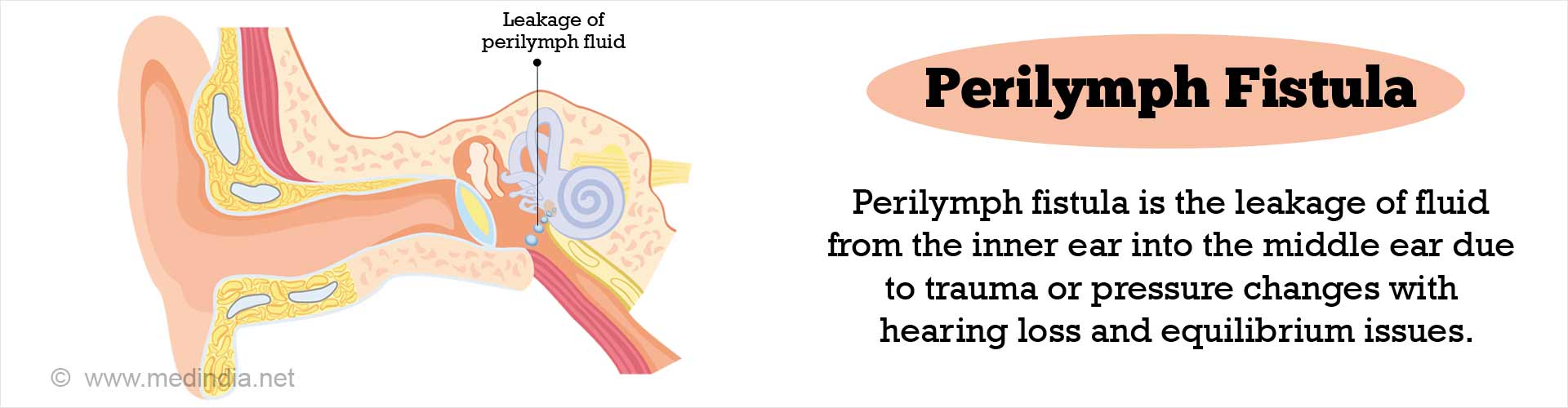
Perilymph fistula is leakage of perilymph fluid from the inner ear into the middle ear. In our ears, the middle ear that is located behind the eardrum is separated from the inner ear that contains the organs controlling balance and hearing. There are two windows (oval and round) that separate the middle ear from the inner ear. If for some reason, the fluid in the inner ear leaks through these windows into the middle ear, you find your hearing is affected and, you feel dizzy with problems maintaining balance.
Perilymph fistula can occur both in children and adults. In children, it may occur at birth(congenital). Perilymph fistula may present acutely or suddenly or may be a chronic problem.
- Acute perilymph fistula - The cause for fluid leakage can be attributed to an immediate case of trauma, such as diving or a high-intensity explosion.
- Chronic perilymph fistula - In these cases, you may notice problems that affect mental capabilities (e.g., understanding or communicating), and issues in maintaining balance in posture.
What are the Causes of Perilymph Fistula?
Perilymph fistula results from various reasons:
- Trauma to the brain
- Changes in pressure (also called barotrauma) - when there is an ascent or descent in an airplane, scuba diving, blowing the nose or due to cough
- Spread of a tumor
- Bone fracture - e.g., labyrinth bone
- Surgery on the stapes of the inner ear (stapedectomy)
- During pregnancy labor
- Deformities in the middle ear
- Lifting weights
- Hard Slap to the ear
- Whiplash to the neck during driving accidents
Perilymph fistula is called spontaneous if it occurs due to a pressure difference whose origin is not very clear or due to the rupture of the labyrinth (part of the inner ear, which controls balance). In most cases, it is not known what has caused the problem to occur and so the term “spontaneous”.