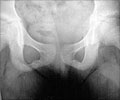
Diagnosis of Infantile Cortical Hyperostosis
The clinical features suggest a
The condition has been occasionally diagnosed in the womb before the birth of a
Most of the bones of the body can be involved however it seldom involves finger bones (phalanges), spine (vertebral bodies) and bones of the hand (cuboidal bones).
The condition should be differentiated from 'battered baby syndrome' (due to child abuse) as bony trauma is the most frequent x-ray finding in child abuse. In child abuse the limb bones are commonly affected. Most of these children are below the age of one year.