- Modern Management of the Exstrophy-Epispadias Complex - (http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/587064)
- Manipal Manual of Surgery 4th edition
What is Bladder Exstrophy?
Bladder exstrophy, also called ectopia vesicae, is a developmental anomaly affecting the lower abdominal wall and the urinary bladder. The urinary bladder is a pouch that stores urine in the body. It is located just behind the mid-lower abdominal wall above the pubic bone. In ectopia vesicae, the anterior wall of the bladder and the lower part of the abdominal wall are not well developed.
As a result of the defect, the posterior wall of the bladder can be seen externally just below the region of the umbilicus or belly button. The condition is extremely rare and is seen more often in males as compared to females.
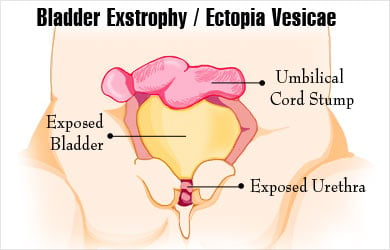
Bladder exstrophy is a part of a group of developmental disorders referred to as exstrophy-epispadias complex. These disorders affect the development of the genital and urinary systems, anterior abdominal wall, and pelvis. They consist of three conditions,
- Epispadias, where the urethra opens in the upper aspect of the penis instead of the tip
- Classic bladder exstrophy
- Cloacal exstrophy, where the bladder as well as the intestines are exposed externally, along with other malformations
Among these, epispadias is the least severe while cloacal exstrophy is the most severe.
Depending on the extent, bladder exstrophy can be classified as:
- Complete bladder exstrophy
- Incomplete bladder exstrophy
In complete bladder exstrophy, developmental anomalies are also noted in the pubic symphysis (joint between the two pubic bones), the penis in males and the clitoris in females. These anomalies are not present in incomplete bladder exstrophy.
Other anomalies like lower digestive tract anomalies as well as spinal anomalies may also be present in complete bladder exstrophy.
What are the Causes of Bladder Exstrophy?
Bladder exstrophy is a genetic condition, which occurs due to a defect in the genes. The reason for this defect has not been established. Some of the factors that could possibly increase the risk of delivering a baby with bladder exstrophy include Caucasian race, young age of mother, multiple prior deliveries of the mother, and conception of the baby following assisted-reproductive technologies. However, more data is required before these factors can be established as definite risk factors for bladder exstrophy.
What are the Symptoms of Bladder Exstrophy?
Patients with bladder exstrophy have the following features depending on the stage at which they present to the doctor:
- Presence of pink to red mucus membrane in the lower middle part of the anterior abdomen
- Constant dribbling of urine, which causes bad smell and damages the skin around the bladder
- Frequent urinary tract infections, which can even result in kidney failure
Other structural features associated with complete bladder exstrophy include:
- The pubic symphysis, the joint between the two pubic bones in the midline, is widely separated.
- The umbilicus or belly button is often absent
- Hernias may be present
- In males, the scrotum is usually normal with the testes in place. The penis may not be well developed and the urethral opening may be present on the upper aspect of the penis instead at the tip.
- In females, the clitoris is usually separated into two and the external genitalia are not well developed
How to Diagnose Bladder Exstrophy?
Diagnosis of bladder exstrophy is based on the history of the patient and physical examination, which reveals the mucus membrane of the bladder externally. Radiological tests are carried out prior to surgical repair. Diagnosis prior to birth is possible using ultrasound.
How do you Treat Bladder Exstrophy?
Constant exposure of the bladder to the external environment can result in complications like frequent urinary tract infections and even cancer. Therefore, it is important to correct the condition surgically.
Bladder exstrophy is treated by surgical repair with closure of the bladder and the anterior abdominal wall. The operation may be carried out in several stages to achieve a near normal appearance and function. In case the bladder does not achieve the required capacity, bladder augmentation procedures may be carried out wherein the size of the bladder is increased with other tissues like the colon or the stomach.
In some cases of complete bladder exstrophy, the urine is drained into the colon, from where it can be eliminated from the body.
Repair of other anomalies like that involving the lower digestive tract and spinal anomalies if present will also need to be corrected.
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA
 Email
Email




