- BK Virus: A Clinical Review - (https://academic.oup.com/cid/article/33/2/191/324706)
- BK virus - (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/BK_virus)
- BK Virus Nephritis after Renal Transplantation - (https://cjasn.asnjournals.org/content/3/Supplement_2/S68.full)
- BK virus in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation recipients. - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19064383)
- BK Virus Nephropathy and Kidney Transplantation - (http://cjasn.asnjournals.org/content/2/Supplement_1/S36.full)
What is BK Virus Infection?
Most of us have already been exposed to BK virus in childhood. Under ordinary circumstances it is unnoticed and rarely causes disease or symptoms. After entering the human body, BK virus spreads via blood and settles silently in the kidneys and sometimes the brain, without noticeably affecting your health.
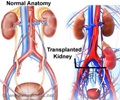
Symptoms of infection from BK virus may arise a persons immunity is compromised.BK virus infections have become more common with use of newer immunosuppressive drugs like cyclosporine, mycophenolate mofetil and tacrolimus to prevent rejection of an organ transplant.
BK virus belongs to the polyomavirus family and was named after a kidney transplant patient in whom it was originally identified.
The BK virus is transmitted via respiratory tract secretions, saliva and urine and from mother to baby during childbirth. After initial infection it remains latent in the blood, kidneys, or other organs of the patient. Transmission from one person to another occurs through fluids like respiratory tract fluids, saliva and urine. The infection can also spread from a mother to her baby during birth.
Risk Factors for Severe BK Virus Infection
Symptomatic flare up due to BK virus infection or reactivation may occur when a persons immunity is decreased in conditions such as:
- Aging:
- Use of potent immunosuppressive drugs in organ transplantation.
- HIV infection and diabetes
What are the Symptoms and Signs of BK Virus Infection?
Initial infection is usually asymptomatic, although sometimes mild symptoms such as fever or body aches may occur. More significant problems listed below, may arise when an infected person's immunity is reduced by use of drugs to manage an organ transplant:
- Brown or red urine due to small amount of blood in the urine
- Difficulties with urination
- Fever, muscle pain or weakness
- Difficulty with breathing, cold and cough
- Worsening kidney function, due to kidney inflammation (interstitial nephritis)
- Overt bleeding and pain with urination due to severe inflammation of the bladder
- Narrowing of the tube that drains urine from bladder to the outside (the urethra) due to scarring
- Pneumonitis and pneumonia due to infection of the lung
- Vision changes
- Seizures
- Rarely, other brain, liver and eye disease
The role of BK virus in causing systemic lupus erythematosus and some cancers has also been suggested.

How do doctors diagnose BK Virus Infection?
The following tests help in confirming the diagnosis of BK virus infection:
- BKV blood test or urine test
- Urinary abnormalities such as presence of decoy cells in urine
- Biopsy of kidney

What are the Treatments for BK Virus Infection?
The main treatment of BK virus infection is reduction in level of immunosuppression by adjusting immunosuppressive medications such as tacrolimus, mycophenolate mofetil, and steroids.
Leflunomide is an antiviral drug with immunosuppressant properties that is often administered to kidney transplant patients with BK infection.
Drugs like cidofovir, another antiviral drug and fluoroquinolones are also used for the treatment of BK virus.
Bladder irrigation is a continuous or intermittent flow of a saline or medicated solution passed through the bladder to wash out unwanted substances from the bladder. Sometimes this procedure may be used to wash out any viral growth in the bladder in case of BK virus infection.
What is the Prognosis of BK Virus Infection?
In otherwise healthy people the presence of BK virus in the body is usually not harmful and the person can remain symptom-free for life. However, if the patient undergoes a
Reduction of immunosuppressive medications is likely to suppress the viral load. Hemorrhagic cystitis (bladder inflammation) can be a challenging problem with BK virus infection. A diagnostic test for the presence of BK virus in blood or urine may be recommended before the surgery for transplantation.
Health Tips
- Prevention of BK virus infection involves identifying the disease with BKV diagnostic tests.
- Before going for an organ transplant it may be necessary to undergo tests to detect BK virus.
- After-transplantation presence of virus will need to be re-assured. Allograft biopsies can help in the detection of BK virus.
- Immunosuppressive therapy must be given with care keeping in mind the possibility of presence of the BK virus in the patient’s blood and kidneys.
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA
 Email
Email