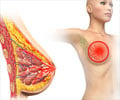
Breast cancer in women are more likely due to pathogenic variants in protein coding genes BARD1 and RAD51D. The changes in DNA creates negative impact and fails to function normally.

TOP INSIGHT
Not all, but certain pathogenic variant genes like BARD1 and RAD51D are responsible for increasing the risk of breast cancer in women.
Dr. Couch and his colleagues studied data from 65,000 women with breast cancer to obtain risk estimates associated with 21 cancer predisposition genes from testing panels.
They found that pathogenic variants in certain genes, such as BARD1 and RAD51D, caused moderately increased risks of breast cancer.
These researchers also confirmed the involvement of the ATM, CHEK2 and PALB2 genes in breast cancer.
They also found that the RAD50 and MRE11A genes did not increase risks of breast cancer.
Dr. Couch also said, "I am hopeful this work will lead to much better interpretation of results from clinical, hereditary [and] genetic testing."
Source-Eurekalert
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA


 Email
Email