Scorpion venom could be a potentially life-saving treatment for heart attack patients as the venom contains a peptide that has a beneficial effect on the cardiovascular system, reveals a new study.
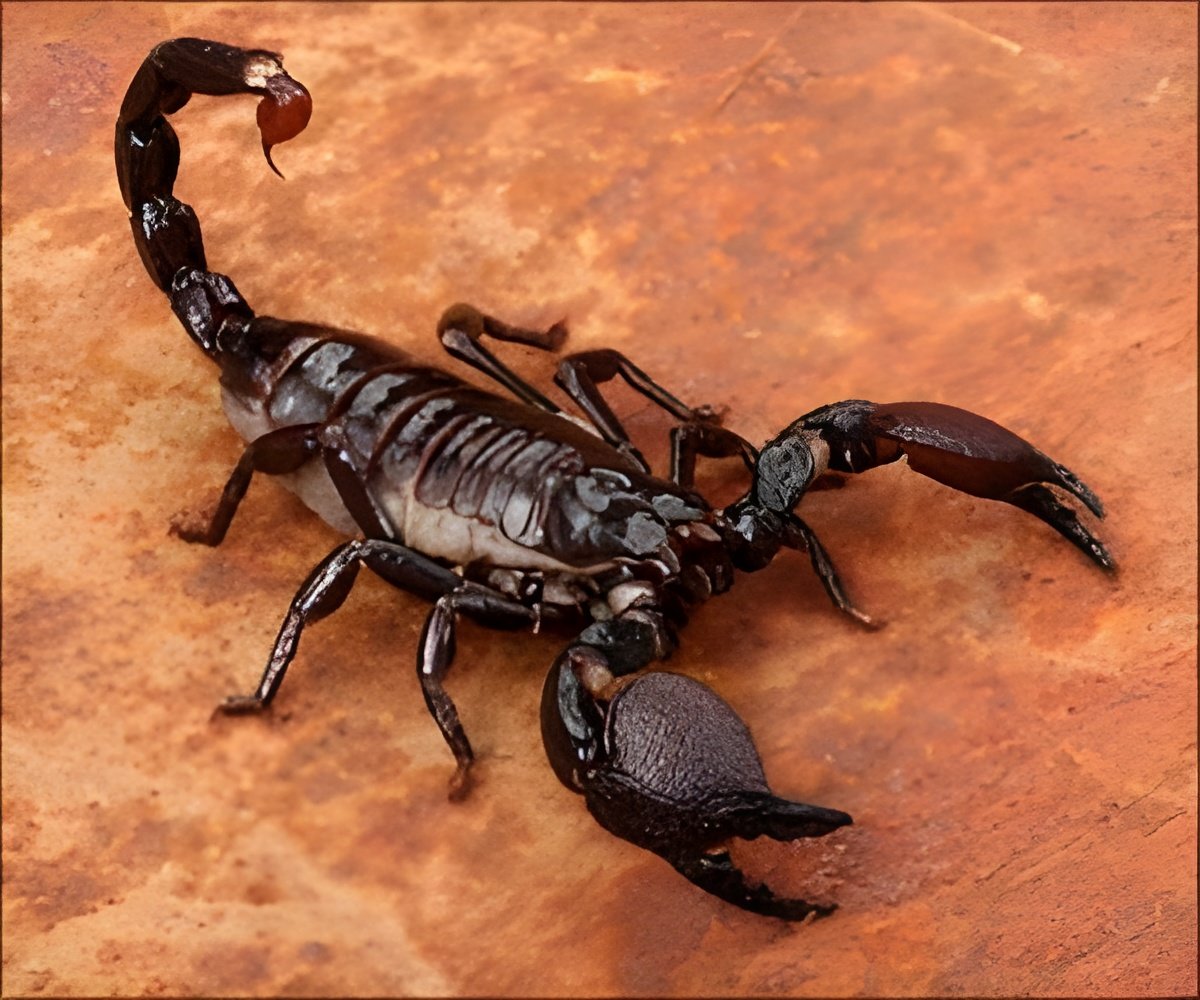

‘Scorpion venom is a complex blend of biologically active molecules, including neurotoxins, vasodilators, and antimicrobial compounds.
’
Read More..




Scorpion venom is painful for those unlucky enough to be stung by a scorpion, individual venom compounds, if isolated and administered at the proper dose, could have surprising health benefits. One promising compound is the tripeptide KPP (Lys-Pro-Pro), which is a piece of a larger scorpion toxin. KPP was shown to cause blood vessels to dilate and blood pressure to decline in hypertensive rats. Thiago Verano-Braga, Adriano Pimenta, and colleagues wanted to find out what exactly KPP does to heart muscle cells. The answer could explain the peptide's beneficial effects. Read More..
The researchers treated mouse cardiac muscle cells in a petri dish with KPP and measured the proteins expressed at different times using mass spectrometry.
They found that KPP regulated proteins associated with cell death, energy production, muscle contraction, and protein turnover. In addition, the scorpion peptide triggered the phosphorylation of a mouse protein called AKT, which activated it and another protein involved in the production of nitric oxide, a vasodilator. KPP treatment, however, caused dephosphorylation of a protein called phospholamban, leading to reduced contraction of cardiac muscle cells. Both AKT and phospholamban are already known to protect cardiac tissue from injuries caused by a lack of oxygen. These results suggest that KPP should be further investigated as a drug lead for heart attacks and other cardiovascular problems, the researchers say.
Source-Eurekalert