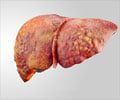
The fifth most common malignancy globally and the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths happens to be hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Type 2 diabetes mellitus has been associated with HCC. However, the relationship between type 2 diabetes mellitus and the underlying liver cirrhosis, and the effects of antidiabetic therapy on HCC risk have not yet been fully evaluated.A research team led by Dr. Valter Donadon from Pordenone Hospital addressed this question. Their study will be published on May 28, 2009 in the World Journal of Gastroenterology.
Four hundred and sixty five HCC patients, 618 cirrhosis patients and 490 control subjects were enrolled in this study. They evaluated the odds ratio (OR) for HCC by univariate and multivariate analysis. Moreover, OR for HCC in diabetic subjects treated with insulin or sulphanylureas and with metformin were calculated.
The prevalence of diabetes mellitus was 31.2% in HCC, 23.3% in cirrhotic patients and 12.7% in the Control group. By univariate and multivariate analysis, the OR for HCC in diabetic patients were respectively 3.12 (95%CI: 2.2-4.4, P < 0.001) and 2.2 (95%CI: 1.2-4.4, P = 0.01). In 84.9% of cases, type 2 diabetes mellitus was present before the diagnosis of HCC. Moreover, we report an OR for HCC of 2.99 (95%CI: 1.34-6.65, P = 0.007) in diabetic patients treated with insulin or sulphanylureas, and an OR of 0.33 (CI 0.1-0.7, P = 0.006) in diabetic patients treated with metformin.
This study demonstrates that type 2 diabetes mellitus is an independent risk factor for HCC and pre-exists in the majority of HCC patients. In male HCC, patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, their data shows a direct association of HCC risk with insulin and sulphanylureas treatment and an inverse relationship with metformin therapy.
Advertisement
RAS