In the realm of precision medicine, there is optimism for tailoring treatments for individuals with irritable bowel disease.
Pathogenesis and precision medicine for predicting response in inflammatory bowel disease: advances and future directions
Go to source) Factors associated with a Western lifestyle such as urbanization, high animal protein intake, ultra-processed foods, and reduced fiber consumption are linked to IBD onset. Gut microbial diversity also plays a key role, with rural communities exhibiting greater microbial richness compared to urban populations. Understanding these environmental and microbial influences is crucial for developing preventive strategies.
‘Embracing personalized strategies holds the key to a more promising future for individuals living with irritable bowel disease. #IBD #Crohn's #ulcerativecolitis #personalizedmedicine’





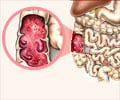
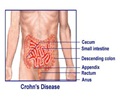
Despite significant scientific advancements, the exact causes of UC and CD remain elusive. A complex interplay of genetics, immune dysregulation, gut microbiota alterations, and environmental factors contributes to disease development. Current immunosuppressive treatment options require more personalized approaches.
Multiomics Analysis and Machine Learning in Irritable Bowel Disease
We can potentially predict treatment response and optimize therapy selection by analyzing individual genetic, immunological, and microbial profiles. This "multiomics" approach, coupled with machine learning, holds the key to unlocking new therapeutic targets and improving patient outcomes.This review dives deeper into IBD's genetic, immunological, and microbial drivers, highlighting potential predictive markers of treatment response. We explore the principles of machine-learning-powered bioinformatics and collaborative research, paving the way for future precision medicine strategies in IBD.
Reference:
- Pathogenesis and precision medicine for predicting response in inflammatory bowel disease: advances and future directions - (https://egastroenterology.bmj.com/lookup/doi/10.1136/egastro-2023-100006)