Septin - a cytoskeletal protein is deployed by human cells to lock up Shigella bacteria that causes potentially fatal human diarrhea.
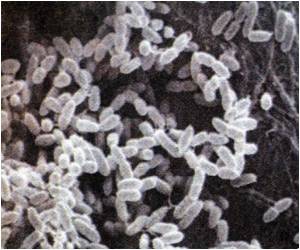
Shigella requires actin to rocket around the host cell before punching into an adjacent cell, said the Pasteur researchers, who made their discovery in human cells grown in culture in the laboratory.
First discovered in yeast as rings that pinch off dividing cells, septins are Guanosine-5'-triphosphate (GTP)-binding proteins that are integral to a cell's dynamic skeleton.
Cossart, a Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI) investigator, and Mostowy continue to investigate the properties of the individual septins, which total 14 in humans, to understand how they associate with other proteins as parts of complex nano-machines.
The study was recently presented at the American Society for Cell Biology Annual Meeting (ASCB) in Denver.
Source-ANI
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA

 Email
Email





