A possible mechanism behind the fibrosis that occurs in scleroderma has been identified by researchers.

TOP INSIGHT
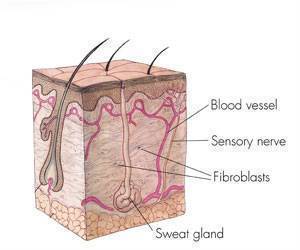
Loss of adipose-derived stromal cells (ADSCs) may contribute to the skin fibrosis characteristic of scleroderma.
Moreover, the study authors found that the survival of those ADSCs that do remain beneath the skin in scleroderma are dependent on immune cells called "dendritic cells." Dendritic cells release a compound called lymphotoxin B that promotes ADSC survival; when antibodies that stimulate the lymphotoxin B receptor were administered with ADSCs to replenish the lost ADSCs, ADSC survival was found to be increased, suggesting a means for reversing the fibrosis of the skin.
"Injecting ADSCs is being tried in scleroderma; the possibility of stimulating the lymphotoxin B pathway to increase the survival of these stem cells is very exciting," says lead study author Theresa T. Lu. "By uncovering these mechanisms and targeting them with treatments, perhaps one day we can better treat the disease."
Dr. Lu also feels this strategy could be used to target stem-cells from other tissue sources in order to treat rheumatological and other conditions - such as lupus and rheumatoid arthritis - and also to facilitate bone and cartilage repair.
In the coming years, Dr. Lu and her colleagues hope to test the applicability of their work in human cells, which could provide scleroderma patients with a welcome treatment option if proven safe and effective. "Improving ADSC therapy would be a major benefit to the field of rheumatology and to patients suffering from scleroderma," she says.
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA


 Email
Email