A novel antiviral drug is found to increase the effectiveness of hepatitis C treatment and improve the cure rate in severe patients, a study has revealed.

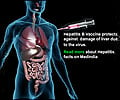
Hepatitis C infections occur mainly through transmission of infected blood, such as via injection drug use, and there is no vaccine. It is a leading cause of liver cancer and liver transplantation.
Adding the drug boceprevir increased the cure rate to as high as 75 percent in those who received 48 weeks of the three-drug combination therapy.
These patients tested negative for evidence of the virus six months after the end of treatment.
"Based on this phase 2 study, it appears that if this drug receives final approval approximately two-thirds of patients will be able to be treated successfully with 28 weeks of treatment and one-third will need 48 weeks of treatment, though this will require confirmation from the phase 3 trials, from which preliminary results were recently released," said Kwo.
The study is published Monday in the online edition of the journal The Lancet.
Advertisement