Bleeding in the brain of a heavy metal fan was found after a night of headbanging at a Motorhead concert, doctors in Germany reported on Friday.
But for the unnamed 50-year-old fan, the concert was followed by constantly worsening headaches.
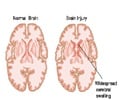
Neurosurgeons at the Hanover Medical School found a small area of bleeding on the right side of his brain called a chronic subdural haematoma, where blood gathers under the outer membrane of the brain.
Invented during heavy metal's 1970s heyday, headbanging has from time to time been associated with health scares such as whiplash and fractures of a cervical bone called the odontoid.
But the Hanover doctors suggest the risk could be somewhat greater.
They trawled through science publications and found three other cases of subdural haematoma caused by headbanging, one of which caused sudden death.
The Lancet, which reported the January 2013 case, said the patient was otherwise healthy, had no history of head injuries and denied any drug abuse.
He may also have had a tiny cyst at that spot, which would have helped rupture the vessels.
The patient underwent keyhole surgery to drain the bleeding and was discharged after eight days. His headaches subsided and a check two months later gave him the all-clear.
"This case serves as evidence in support of Motorhead's reputation as one of the most hardcore rock'n'roll acts on Earth, if nothing else because of their music's contagious speed drive and the hazardous potential for headbanging fans to suffer brain injury," the doctor said.
Source-AFP
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA



 Email
Email