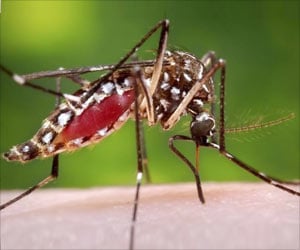
A single mosquito bite can affect the immune system for a week, finds study.

TOP INSIGHT
Components in the mosquito saliva can trigger an unexpected and long-lasting immune responses.
"We found that mosquito-delivered saliva induced a varied and complex immune response we were not anticipating," said Silke Paust, Assistant Professor at Baylor and Texas Children's Hospital.
"Billions of people worldwide are exposed to diseases transmitted by mosquitoes, and many of these conditions do not have effective treatments," added Rebecca Rico-Hesse, Professor at the Baylor College of Medicine in Texas, US.
For the study, appearing in the journal PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases, the team worked with a mouse model of the human immune system.
Previously, the team demonstrated that mosquito-bite delivery and needle-injection delivery of dengue virus in these "humanised mice" led to significantly different disease developments
In the new study, the team tested the effect of virus-free mosquito saliva on humanised mice and compared the results with those obtained from humanised mice that had not been bitten by mosquitoes.
"For instance, both the immune cell responses and the cytokine levels were affected. We saw activation of T helper cells 1, which generally contribute to antiviral immunity, as well as activation of T helper cells 2, which have been linked to allergic responses," Paust said.
"The diversity of the immune response was most striking to me. This is surprising given that no actual infection with any type of infectious agent occurred," he noted.
Source-IANS
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA



 Email
Email








