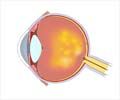
Due to the aging population, an increasing number of patients are being treated for age-related macular degeneration (AMD), an eye condition in which abnormal blood vessels develop and leak into the eye. When patients develop wet AMD, they receive injections of anti-vascular endothelial growth factor medication (VEGF). VEGF prompts growth of new blood vessels in the body. In the case of AMD, however, such new growth is unwanted and may cause bleeding in the retina.
It has not been clear whether this treatment would also serve patients experiencing other symptoms, such as vitreomacular interface disease (VMID), in which there is traction or contact between the retina and the vitreous matter in the eye. Mayo researchers retrospectively studied 178 patients, of whom 18 percent had VMID over an average of 2.5 years.
Findings showed that while eyes with some kind of macular traction required more injections, they still showed improvement (best corrected visual acuity) to similar eyes without VMID.
"This finding is significant," says senior author Sophie J. Bakri, M.D., "because it showed that patients with VMID are not necessarily treatment resistant for AMD." She also says it may help physicians not give up on treating such patients, and understand the need for more doses of medication for those with VMID. Researchers say more study is needed, including a prospective clinical trial.
Co-authors include Amy Green-Simms, M.D., Blake Fechtel and Zubin Agarwal, M.P.H., all of Mayo Clinic. The research was funded in part by Research to Prevent Blindness.
Advertisement