Neurons can utilize a supremely localized internal store of calcium for communicating with each other and other cells, reveal researchers.
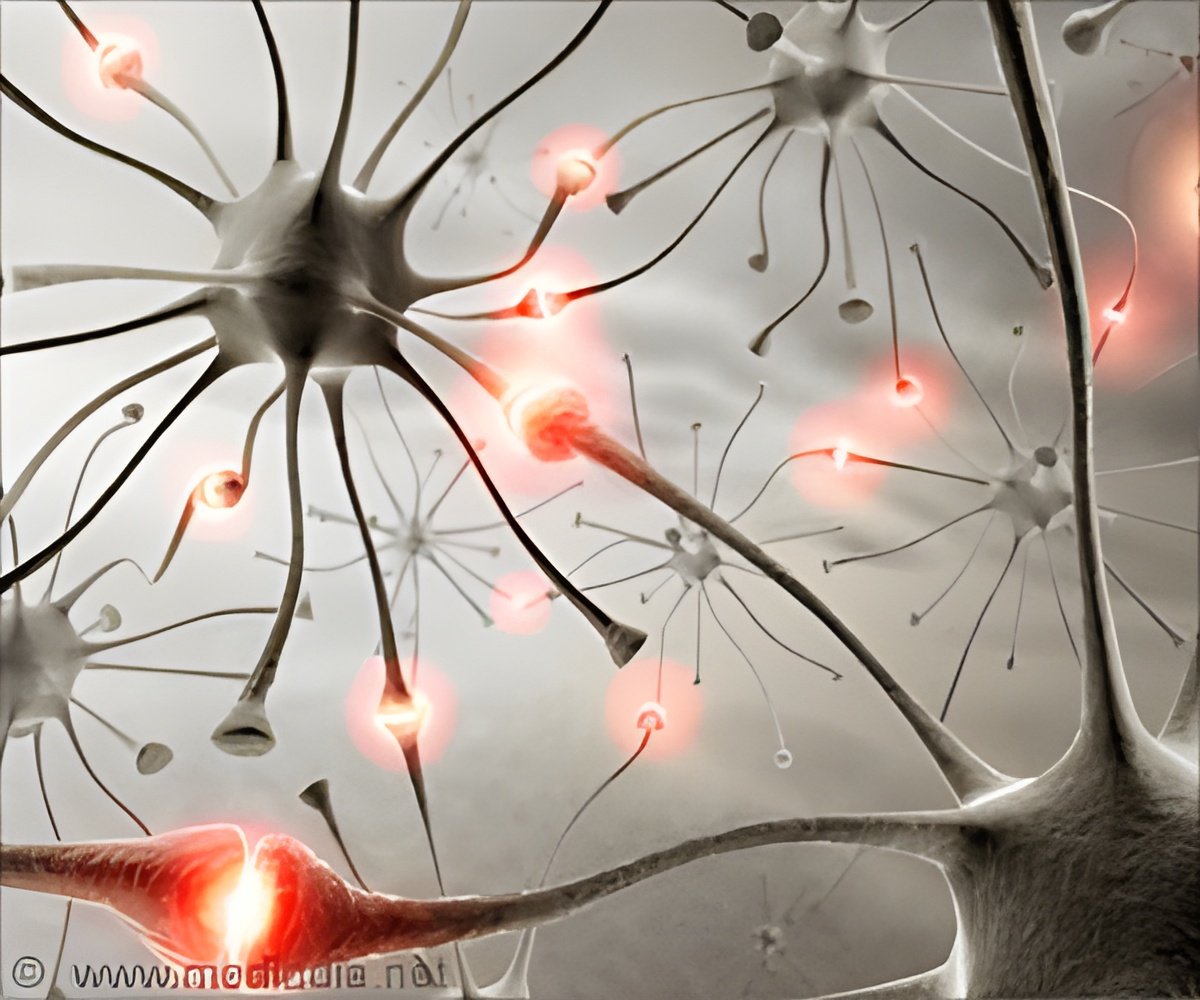
A team of researchers led by José Lemos from the University of Massachusetts Medical School examined the mechanisms at play during secretion of vasopressin from nerve terminals in the posterior pituitary gland, which releases the neuropeptide into the blood so that it can make its way to the kidney and regulate water retention. The researchers found that certain intracellular calcium channels known as ryanodine receptors are likely responsible for mobilizing calcium from LDCVs to facilitate vasopressin release. The findings indicate that neurons have a greater capacity than previously appreciated to fine-tune the release of neuropeptides and thereby their communications with other cells.
Source-Eurekalert
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA



 Email
Email










