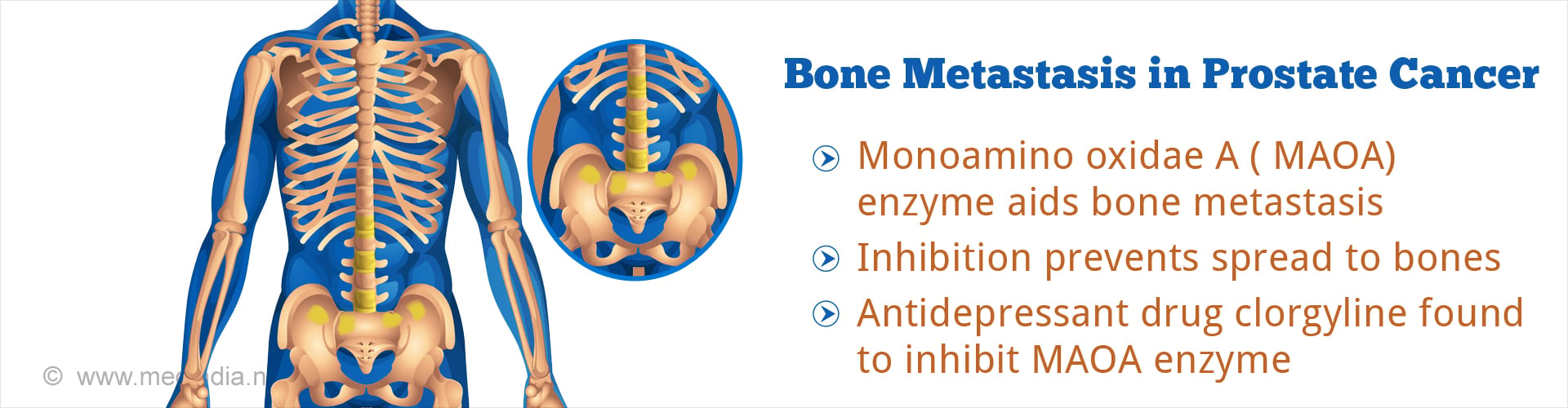
Mechanism of Bone Metastasis in Prostate Cancer Patients Identified
- This is the first study to discover the effectiveness of the antidepressant drug clorgyline in inhibiting Monoamine oxidase A (MAOA) enzyme
- MAOA enzyme is shown to increase bone metastasis in prostate cancer patients, resulting in poor bone health and risk of fracture
- Since the drug clorgyline is already in use as an antidepressant, it could potentially decrease the time required to carry out clinical trials
TOP INSIGHT
Monoamine oxidase A (MAOA) enzyme is a potential target for drug therapy among prostate cancer patients to prevent bone metastasis.
Bone Degradation Due to Enzyme Activation
Dr. Wu and his colleagues identified a specific enzyme, called Monoamine oxidase A (MAOA), which leads to the activation of a string of signals, which facilitated easier invasion of tumor cells into the bone. Osteoblasts are a type of cells that build the bone. These cells are then reabsorbed during growth. In the event of damage to the cells, healing is initiated by the osteoclasts. The enzyme MAOA initiates three proteins, which increase the activity of the destructive osteoclasts.Dr. Wu stated that the cancer cells were found to specifically activate the osteoclasts into degrading the bone. In the study carried out by the research team, it was observed that there was more bone destruction than bone development. The results were found to be consistent even when several different human cancer lines were used in mice.
The scientists found that
- On lowered expression of these enzymes in prostate cancer cells, there was a lower bone metastasis of prostate cancer.
- On overexpression of these enzymes in prostate cancer cells, there was increased bone metastasis in mice.
Effect of Antidepressant Enzymes
The scientists stopped the activity of the enzyme MAOA with a drug called clorgyline, which is used to disrupt signals that result in cancer cell invasion and proliferation. These drugs are used as antidepressants while there is an ongoing research on their use as drugs for tumor.There are no studies that have detailed the reduction in prostate cancer risk among people who take antidepressants. The current study provides results that are promising and which substantiate the need for further testing and analysis.
Prostate Cancer and Bone Health
Bone associated problems are faced by many patients with prostate cancer due to the spread of the disease. This is known to result in- Severe pain
- Fracture
- Bone loss
- Joint pain
Treatment to Maintain Good Bone Health
As prostate cancer can affect bone health, it is necessary to develop strategies that aid in maintaining good bone health. The current study has identified a method of preventing bone health from being affected due to prostate cancer, which can improve the quality of life lead by the patient.MAOA Enzyme
Monoamine oxidase A (MAOA) enzyme, also called as the warrior gene, degrades amine neurotransmitters like norepinephrine, serotonin and dopamine. It is a flavoenzyme and regulates normal brain function. The enzyme localizes to the outer mitochondrial membrane but is expressed highly in the cardiac and neural cells. Transcription factors GATA, SP1 and TBP mediate the expression of this enzyme in response to stress like inflammation and ischemia.The significance of MAOA in cancer is that it produces an amine oxidase that aids in carcinogenesis. The drug Clorgyline, is an MAOA enzyme inhibitor and has been shown to lead to apoptosis in melanoma cell lines. The current study is the first study that has identified the importance of the drug in animal studies.
Benefits of the Study
The study showed that MAOA played an important role in bone deterioration among prostate cancer patients and that lower amount of the enzyme was associated with lower bone metastasis. Inhibition of MAOA enzyme in animal studies has been shown to prevent bone metastasis, which was done using clorgyline. Since clorgyline is a drug which is already approved as an antidepressant, the new benefits associated with this drug would aid in faster utilization in clinical studies.References:
- Bone Metastasis - (https://zerocancer.org/learn/current-patients/advanced-cancer/prostate-cancer-metastasis/bone-health/)
- Advanced prostate cancer: Managing symptoms - (http://prostatecanceruk.org/prostate-information/advanced-prostate-cancer/advanced-prostate-cancer-managing-symptoms)
Source-Medindia
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA

 Email
Email