Scientists have developed an inexpensive biosensor which can be used to detect even trace amounts of glucose thus enabling early detection.
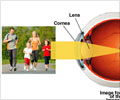
- Transparent biosensors developed using low cost semiconductor material have been embedded on contact lenses to detect glucose levels
- These can be worn by the patient and will help in continuous monitoring of the patient
- The biosensors will help in early detection of illnesses
TOP INSIGHT
Biosensor contact lenses are designed to detect very small quantities of glucose making the suitable for early diagnosis and continuous monitoring
Touch Screen Sensitivity and Biosensors
The concept of developing a biosensor occurred to Dr.Herman while he worked in an industrial set up, revolutionizing electronics by teaming up with two of his colleagues to develop the compound composed of indium gallium zinc oxide (IGZO). This semiconductor offered consumers high quality displays with superior resolution for smartphones, televisions and tablets, enhancing touch screen sensitivity and saving power.Dr. Herman moved to Oregon University and began to delve deeper into the biomedical aspects of this semiconductor technology. He was motivated to find a method by which people with diabetes could monitor their sugar level continuously using these biosensor lenses.
Limitations in the Current Method of Diabetes Detection
- A small ‘prick and blood test’ is currently used to monitor blood sugar levels. The method is invasive and continuous monitoring is not possible. Moreover, pricking too often can be tiresome.
- Continuous glucose monitoring normally requires the use of electrodes that are inserted into the skin at various sites, which is painful or could lead to skin irritations.
Advantages of Bio-sensing Contact Lenses
Dr. Herman stated that the limitations associated with the current methods of testing could be eliminated with bio-sensing contact lenses.- They can be used for continuous monitoring
- They are non-invasive
- Compliance could be improved as the individual can replace it every day
- They are transparent which will not make the individual self-conscious
The electrical changes that occur when used in conventional biosensors can be used to measure the glucose concentrations present in the interstitial fluid present below the skin of the patient. However, the glucose concentrations present in the eye are very low. To overcome the low levels of glucose, the IGZO biosensors were designed with nanostructures which are highly sensitive to trace even small amounts of glucose.
Previous studies with the biosensors involve its use to indicate kidney function by measuring uric acid. It could take another year before this biosensor can be used for animal studies. The biosensor can also be used for efficient delivery of drugs, especially for ocular conditions.
Biosensors to detect glucose Levels in saliva
Biosensors are being carefully designed to improve technology based medical diagnosis. A research team from Hong Kong Polytechnic University developed a biosensor which was sensitive to glucose. This biosensor detects the level of glucose by identifying the electric current In the saliva.This biosensor was found to detect glucose levels that were as low as 10-5mmol/L which is a lot more sensitive than conventional methods of detection. They are cost effective and can even be used on human skin and as wearable technology.
There are several other biosensors that are being keenly developed like the uric acid sensors and the cholesterol sensor. These sensors are revolutionizing medical diagnosis and will help in detecting medical conditions early, sometimes even before the symptoms actually set it.
Reference:
- Highly sensitive biosensor for measuring glucose in saliva - (https://phys.org/news/2016-04-highly-sensitive-biosensor-glucose-saliva.html)
- Smart contact lens and smart eye glasses - (http://www.frontiersin.org/10.3389/conf.FBIOE.2016.01.01493/2893/10th_World_Biomaterials_Congress/all_events/event_abstract)
Source-Medindia
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA




 Email
Email