The microorganisms found in the gut were found to alleviate symptoms of autoimmune disorder IPEX syndrome, providing a possible cure for the condition.
- Faulty T-cells lead to inflammation that results in autoimmune disorder.
- Replacing the gut microbiota and introduction of inosine found to cure autoimmune disorder IPEX syndrome.
- Gut microbes play a key role in maintaining health and could also aid in treating autoimmune disorder.
TOP INSIGHT
Gut microbes could play a key role in the management of autoimmune disorders.
Gut Microbiome and Gastrointestinal Disorder
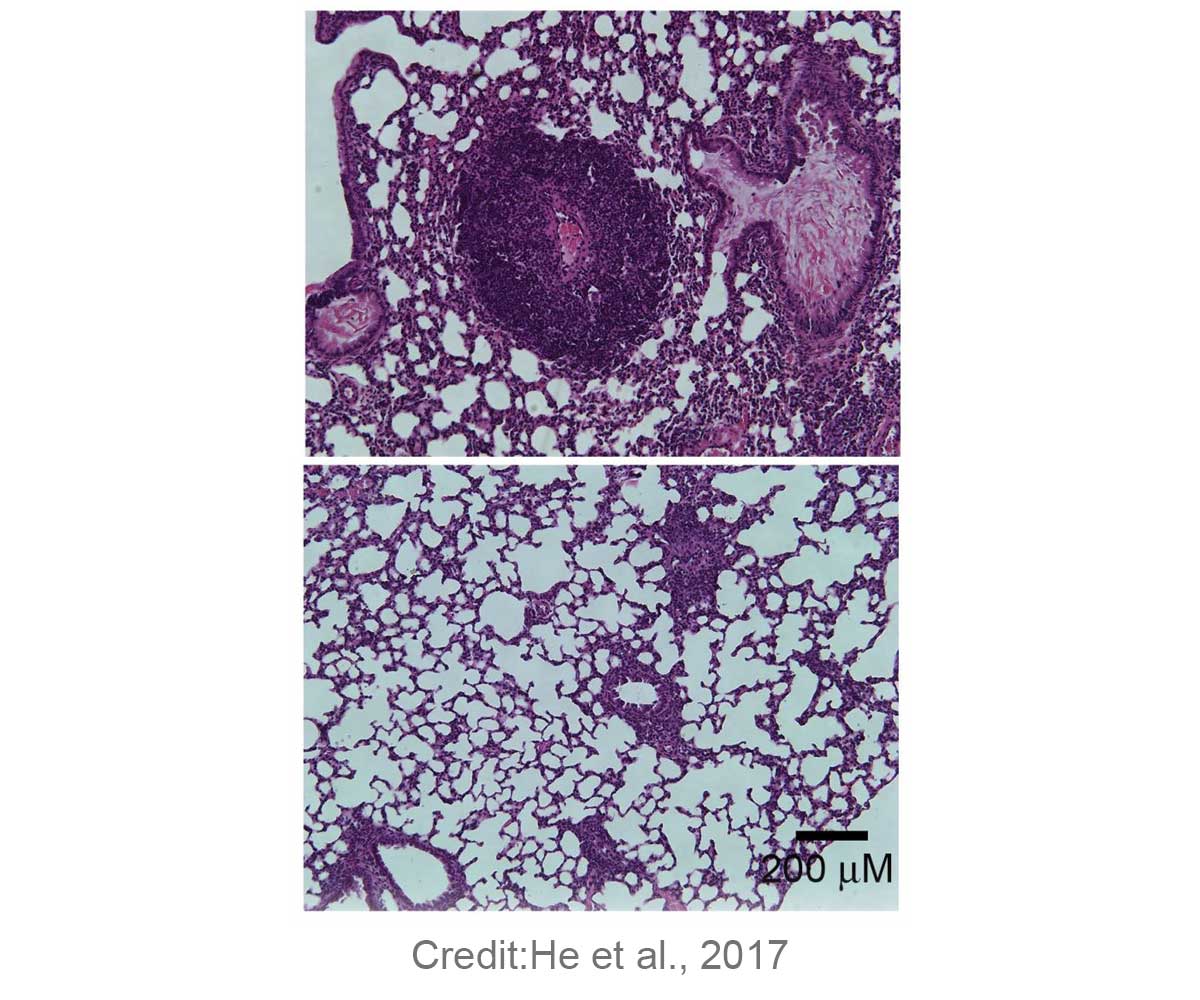
The gut microbiome can also result in an autoimmune disorder, according to the study by Yuying Liu and J. Marc Rhoads from The University of Texas Health Science Center. Disruptions in the Foxp3 transcription factor were found to disrupt the regulation of the T-cells which, lead to the development of IPEX syndrome.Mice that carried a mutant version of the Foxp3 gene were found to
- Show changes in the gut microbiome
- At the same time there was development of autoimmune disorder
- The mice had lower levels of lactobacilli
- When the mice were fed with Lactobacilli reuteri, the level of inflammation was lowered
Yuying Liu added that "Our findings suggest that probiotic L. reuteri, inosine, or other A2A receptor agonists could be used therapeutically to control T cell-mediated autoimmunity."
IPEX Syndrome
Immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, X-linked (IPEX) syndrome is a group of autoimmune disordersthat affect many parts of the body. Males are more often affected than females but it is fatal during early childhood.
Diet Found to Influence Autoimmune Disease via Gut Microbes
The study by Dr. Thirumala-Devi Kanneganti from St. Jude’s hospital showed that the diet consumed influences the type of bacteria that grow in our gut, which in turn influence autoimmune disorder. Mice that had a condition that was similar to chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis were fed with a normal diet, they developed enlarged lymph nodes, bone erosion and hind paw inflammation within a period of 100 days.
When the mutant mice were fed with a diet that was rich in saturated fat and cholesterol, they were protected from the effects of the autoimmune condition. This study shows that gut microbes can play a beneficial role in autoimmune disorders.
Gut Bacteria Could Cause Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease that results in pain in the joints and inflammation. Over a period of time, it could lead to damage to the lungs and to the kidney. This autoimmune condition can occur at any stage with the reason unknown. In a previous study, it was found that people who were detected with rheumatoid arthritis showed that Prevotella copri was found in 75% of the patient’s intestine.
These studies show that the type of microbes that are present in our gut could either aid us in lowering the effect of an autoimmune condition or could trigger the condition. The colonization of harmful bacteria may be avoided by enriching the gut with good bacteria.
Yogurt and probiotic products are rich in ‘good bacteria’, the ones that will prevent unnecessary immune reaction that form the basis of autoimmunity.
References:
- Immune Dysregulation, Polyendocrinopathy, Enteropathy, x-Linked Syndrome - (https://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/condition/immune-dysregulation-polyendocrinopathy-enteropathy-x-linked-syndrome)
- Diet Affects Autoinflammatory Disease Via Gut Microbes - (https://www.nih.gov/news-events/nih-research-matters/diet-affects-autoinflammatory-disease-gut-microbes)
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA


 Email
Email