Modifying heart dysfunction may be benefit in the treatment of COPD patients.
Our body’s nervous system has two major components that are called the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system, consists of the brain and the spinal cord and the peripheral nervous system in turn consists of the somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system. The somatic nervous system is responsible for all voluntary muscle contractions and sensory stimuli (touch, smell, hearing etc,) while the autonomic nervous system controls all the involuntary functions of the body such as breathing,digestion, control of blood pressure, sugar and many more functions. The ANS has two sections - one that accelaerates the ANS functions (sympathetic) and the other that brakes some of the body functions (parasympathetic).
According to the new findings, autonomic nervous system (ANS) dysfunction plays an important role in decreasing the quality of life. Dysfunction of the ANS is known to explain a wide range of physical and physiological illnesses.
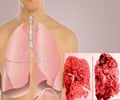
A clear cut understanding of the factors contributing to the poor quality of life in patients with lung disease such as COPD can definitely improve their health status. Unfortunately very little research has been done till date.
The latest study published in the journal ‘Respirology’ described 60 patients with COPD. The patients included in the study were clinically stable ones and aged 40 to 75 years.
Their quality of life was measured through a questionnaire, and their heart rates were measured through Holter electrocardiogram monitoring devices. Lung function was assessed using spirometry, whole-body plethysmography, and diffusion capacity measurements. The Holter electrocardiogram device recorded heart rate variability (HRV), an assessment tool for the functionality of the autonomic nervous system.
Thus it clear that testing the cardiac autonomic function is important for improving the quality of life in patients with Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Treatments that target the autonomic nervous system regulation of the heart can help in overall improvement of patients with chronic lung pathologies like obstructive airway disease.
Source-Medindia
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA

 Email
Email