Lateral Patellofemoral Overload Syndrome is characterized by inflammation or localized knee pain and prominently affects sports persons.
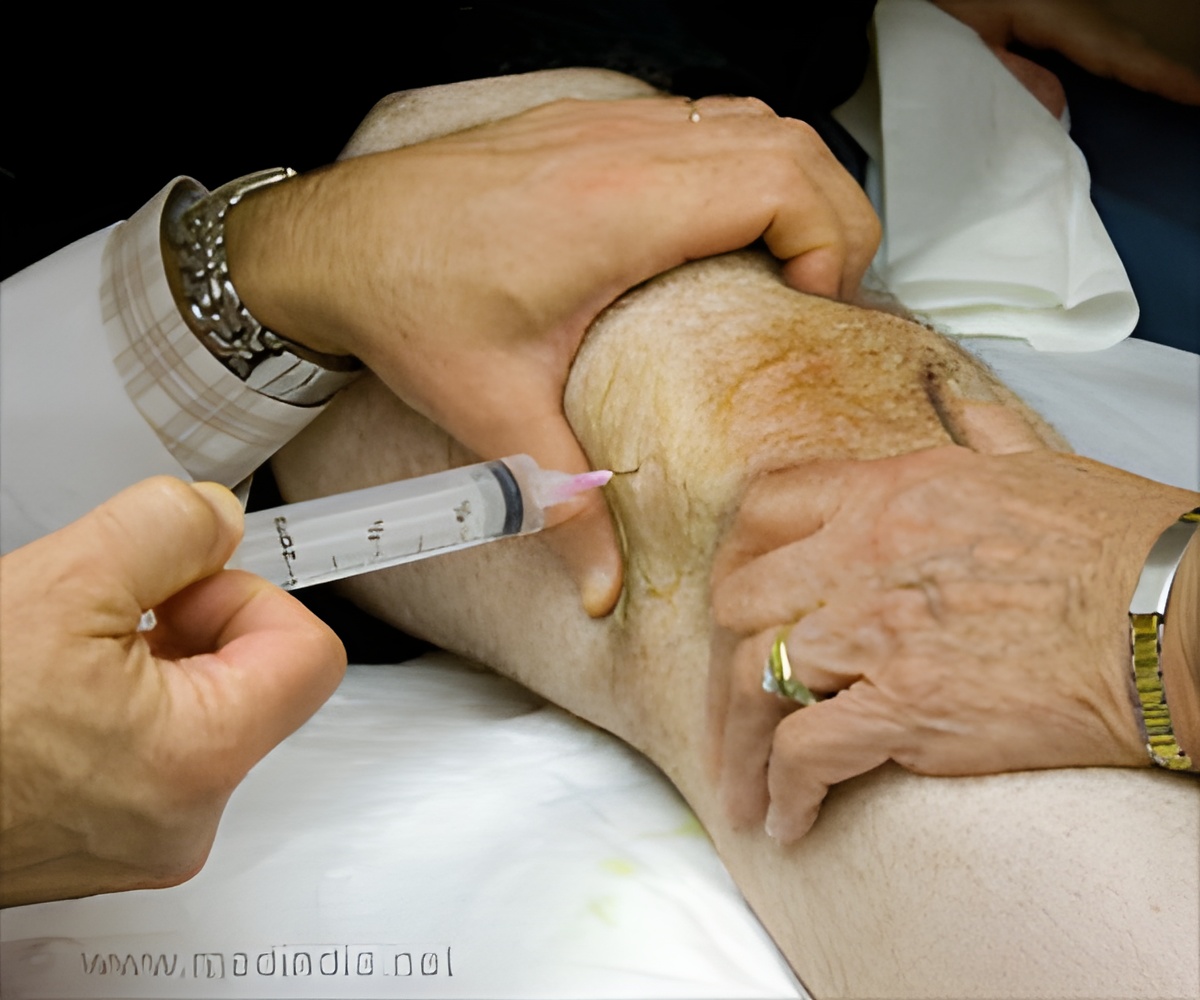
‘The super twin of Botox, Dysport, a type of botulinum toxin may relieve lateral patellofemoral overload syndrome in runners, cyclists and other active people.’





Though these treatments can relieve the pain, athletes report persistent pain and reduced activity after a particular period. Therefore, researchers from Imperial College London and Fortius Clinic have come with a new treatment that can permanently treat the condition.They conducted the study among 45 patients with LPOS, in which the patients were administered with Dysport injection followed by personalized physiotherapy sessions.
Dysport is similar to Botox, a type of botulinum toxin which is prominently used in cosmetic treatments. After this treatment, researchers found that 69 percent of patients required no further medical treatment, and had complete pain relief five years later.
Study co-author Dr.Jo Stephen, of Imperial College London and Fortius, said, "As a physiotherapist it can be incredibly frustrating to run out of treatment options for patients with this painful condition. Many athletes who took part in this study had exhausted all other treatment options and this was their last resort. We are really excited that our approach is showing positive results for patients, which could have implications for active people around the world."
Patients were given personalized physiotherapy to strengthen their buttocks muscles and address other weak or tight muscles after the injection. The study was published in the American Journal of Sports Medicine.
Advertisement
Source-Medindia