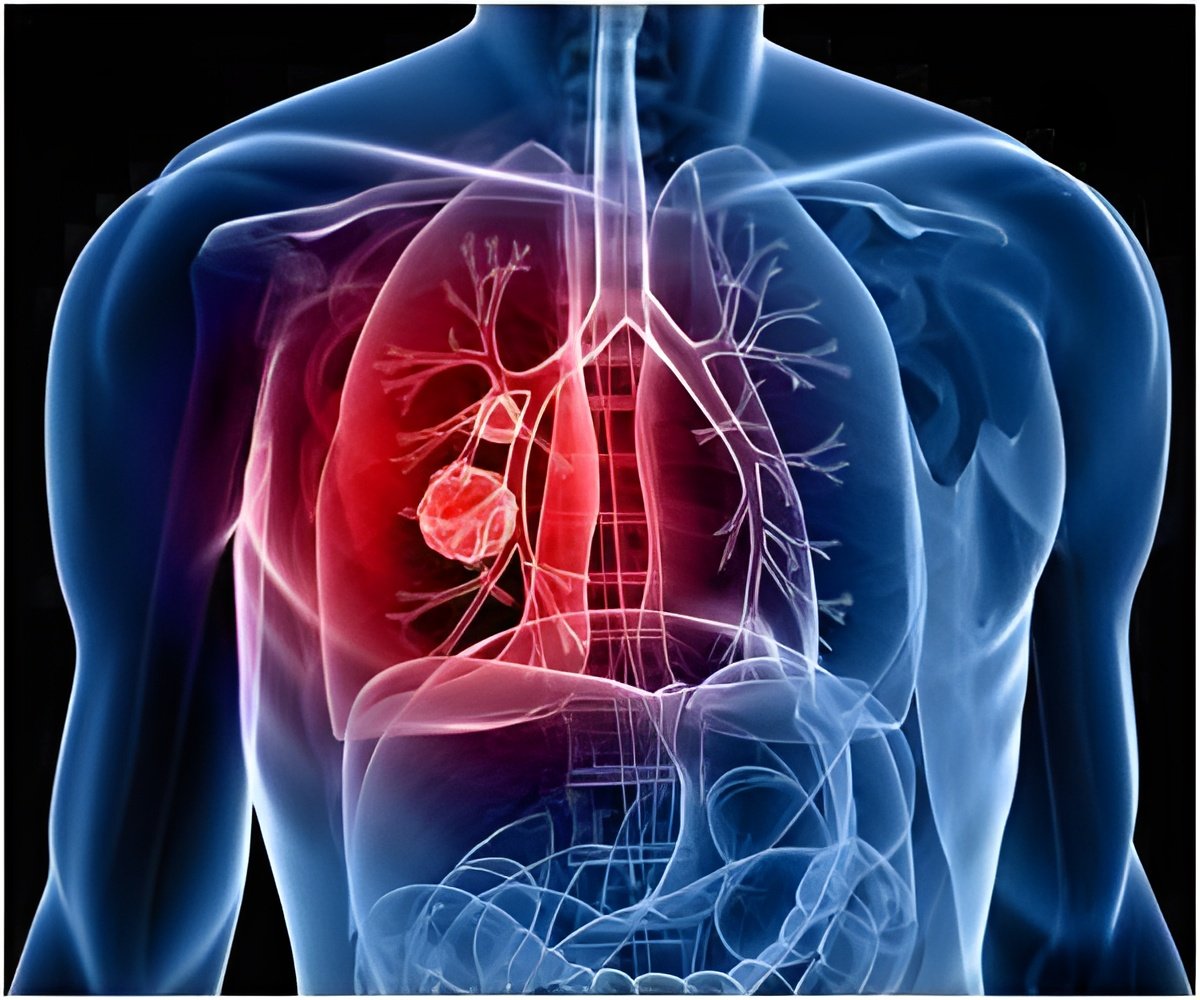
Spread of liver cancer to the lung can be caused by dust cells, also called ‘alveolar macrophages’ (AMs). Dust cells are responsible for the uptake of oxygen and excretion of carbon dioxide in the lung.
TOP INSIGHT
Cells that clean the lung called ‘dust cells’ or ‘alveolar macrophages’ (AMs) may cause the spread of liver cancer to the lung.
"IMs derive from the circulation, and were already known to aid the survival and growth of lung tumors," study first author Takuto Nosaka says. "Conversely, AMs come from tissue lining the inside of air sacs (alveoli) in the lungs, and were only recently shown to be involved in metastasis. Their function in lung metastasis was unclear, but their observed increase in this model is the first evidence that they must play an important role."
Indeed, AMs around the mouse lung nodules produced more of the inflammatory lipid leukotriene B4 (LTB4) than IMs. LTB4 activates immune cells, and directly boosts the proliferation and invasiveness of both human and mouse cancer cells, including HCC cells. AMs were also shown to directly promote tumor cell growth at metastatic lung nodules through LTB4 secretion.
"We next focused on AM recruitment from the bloodstream into the lungs, and showed that this was controlled by IMs which express the signaling molecule CCL2," corresponding author Naofumi Mukaida explains. "The CCL2 receptor, CCR2, is expressed by AMs, and binding of the two molecules controls AM accumulation."
This AM-IM interaction contributes to the progression of lung metastasis through the production of LTB4, suggesting the potential for developing a novel treatment approach that targets these molecules.
The study is published in the Journal of Immunology.
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA
 Email
Email