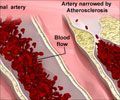
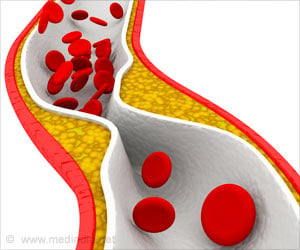
Atherosclerosis could one day be treated with a single shot of synthetically designed nanofibres that help break up as well as reverse the arterial plaque, say researchers.
TOP INSIGHT
A single shot of synthetically designed nanofibres might one day help break up as well as reverse the arterial plaque - making this a hallmark in atherosclerosis treatment, finds a new study.
The results "demonstrate that a novel targeted nanofibre binds specifically to atherosclerotic lesions and reduces plaque burden after a short treatment duration," said lead author Neel A. Mansukhani, an integrated vascular surgery fellow at Northwestern University in Chicago, US.
The findings were presented at the American Heart Association's Vascular Discovery: From Genes to Medicine Scientific Sessions 2018 in San Francisco.
The tiny fibres contained an amino acid sequence that promotes the cholesterol to dissolve and helped remove deposits from the plaque in the artery walls.
To test the noninvasive therapy, mice were genetically modified to rapidly develop atherosclerosis, then fed high fat diets for 14 weeks and after which the mice received biweekly injections of either the peptide amphile nanofibre or saline for 8 weeks.
While drugs such as statins are used to control low density lipoprotein (LDL) the so-called bad cholesterol and thus decrease "plaque burden", "but they have not been proven to reverse the disease", Mansukhani said.
However, more research is needed before this new approach can be tested in humans, he noted.
Source-IANS
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA


 Email
Email