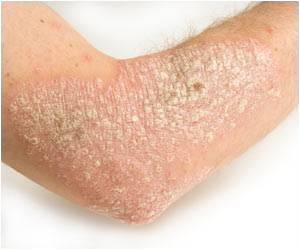
In the Japanese population, eight novel loci associated with susceptibility to atopic dermatitis have been discovered by researchers.

The research group set out to shed light on these origins using a genome-wide association study (GWAS), an approach which identifies gene loci associated with a particular trait. With its strong genetic basis, atopic dermatitis is well suited to the GWAS approach. Three previous GWAS on European and Chinese populations identified 7 loci associated with the condition, but no such studies have been conducted on Japanese people.
To fill this gap, the group conducted a thorough GWAS on 1472 subjects with atopic dermatitis and 7971 controls from among the Japanese population, and then validated their results in a separate study on 1856 subjects with atopic dermatitis and 7021 controls. Analyzing a total of roughly 600,000 genetic variants (called Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms or SNPs), they identified 8 new genetic regions associated with atopic dermatitis and confirmed the 7 loci observed in earlier studies. Among these regions, they identified variants at the IL1RL1/IL18R1/IL18RAP and human leukocyte antigen (HLA) loci, both of which have been associated with bronchial asthma in recent GWAS.
The group's findings thus suggest that atopic dermatitis and asthma have overlapping susceptibility regions, and thus that these regions contain common genetic factors for many allergic diseases. Other loci reveal a wide variety of additional factors possibly involved in the condition, suggesting paths for future research and pointing the way to more effective treatment techniques.
Source-Eurekalert