What is Diabetes?
Diabetes is the most rapidly progressing, non-communicable disease of the 21st century. Diabetes affects 422 million people worldwide, with a dramatic increase in developing countries. In India, about 6 percent of the population suffers from diabetes. By 2025, it is estimated that every fifth diabetic in the world will be an Indian (1✔ ✔Trusted Source
Diabetes
Go to source).
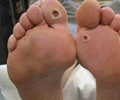
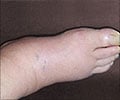
Diabetes is also known as the Iceberg Disease or Silent Disease as the clinical presentation is only a fraction compared to the totality of the disease. It is associated with variable clinical manifestations and many complications. Diabetic foot is one such serious problem. The term diabetic foot comprises a group of ailments ranging from neurological and blood circulatory problems to complications arising from injuries or infections (2✔ ✔Trusted Source
The tip of the iceberg: an overview of diabetic foot disease
Go to source).