Glossary
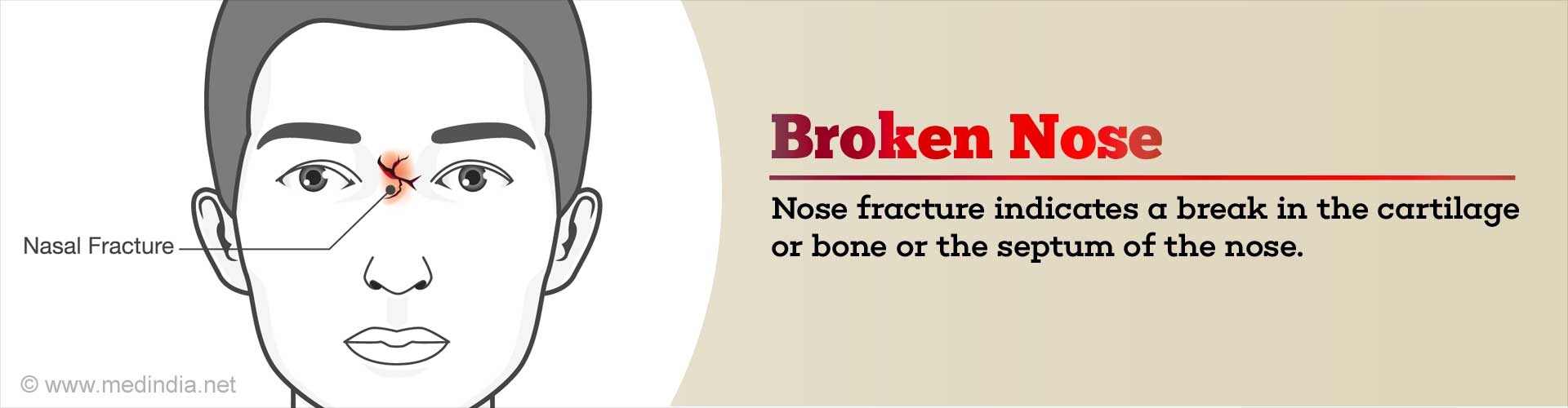
Fracture: A fracture is a break in the bone or cartilage. Fractures are also named by the trauma event that caused the bone breakage.Bone: Bone is the substance that forms the skeleton of the body. It is composed chiefly of calcium phosphate and calcium carbonate. It also serves as a storage area for calcium, playing a large role in calcium balance in the blood.
Cartilage: A type of connective tissue that contains cells (chondrocytes) surrounded by a tough but flexible matrix. The cartilage matrix is made of several types of the protein collagen and several types of proteoglycans, which are combinations of protein and long sugar molecules called glycosaminoglycans. Chondroitin sulfate is the major glycosaminoglycan in cartilage.
Swelling: Abnormal inflammation that occurs in the body.
CT: This is a X- ray procedure enhanced by computer the results are three dimensioned scan through a body part showing bone and body tissue.
X ray: High-energy radiation with waves shorter than those of visible light. X-rays possess the properties of penetrating most substances (to varying extents), of acting on a photographic film or plate (permitting radiography), and of causing a fluorescent screen to give off light (permitting fluoroscopy). In low doses, X-rays are used for making images that help to diagnose disease, and in high doses to treat cancer. Formerly called a Roentgen ray.
Hemorrhage: Bleeding; escape of blood from blood vessels, in microscopic amounts or large volumes.
Radiography: The formation of images of the inside of the body using radiation projected through the body and onto film; a radiograph is also called an X-ray
Acetaminophen: A drug that reduces pain and fever (but not inflammation).
Rhinoplasty: Surgery that changes the structure of the nose, either to improve appearance or to correct a deformity or injury
Headache: Pain or discomfort of the head, upper face, scalp, or neck region
Vomiting: The ejection of contents of the stomach through the mouth.
Giddiness: Feeling faint or unsteady.
Anesthesia: Loss of feeling or sensation resulting from the administration of certain drugs or gases.
Epistaxis: Nosebleed
Bruising: A bruise or "contusion" is an traumatic injury of the soft tissues which results in breakage of the local capillaries and leakage of red blood cells. In the skin it can be seen as a reddish-purple discoloration which does not blanch when pressed upon. When it fades it becomes green and brown as the body metabolizes the blood cells in the skin. It is best treated with local application of a cold pack immediately after injury.
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA
 Email
Email







