- Johnson BA. Flexible Sigmoidoscopy: Screening for Colorectal Cancer. American Family Physician Jan 1999.
What is Flexible sigmoidoscopy?
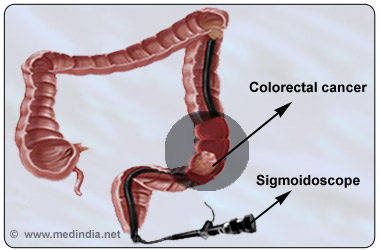
Flexible sigmoidoscopy is an endoscopic procedure used to screen individuals for colorectal cancer suspected to be in sigmoid colon.
Compared to colonoscopy flexible sigmoidoscopy, it is a quicker procedure and does not require sedation. However, some polyps or cancers especially in the transverse colon on the right side of the colon could be missed. It is a good test to screen for cancers where there has been diversion of urine into this section of the colon to look for cancers. Normally patients with urinary diversion have some risk of developing cancers after 10 to 15 years of the diversion.
Flexible sigmoidoscopy can also be used to screening people for rectal cancers or cancers in sigmoid. A number of other tests are also available; the details of these could be accessed at the link below:
http://www.medindia.net/health-screening-test/colorectal-cancer-screening.htm
The colon or large intestine comprises of the following parts, the ascending colon, the transverse colon, the descending colon, the sigmoid colon and the rectum. Flexible sigmoidoscopy allows examination of the sigmoid colon, part or full descending colon and rectum.
Flexible sigmoidoscopy is an endoscopic test in which the doctor exams the inner lining of the lower large intestine and rectum through a flexible tube inserted through the anus. The sigmoidoscope has a camera and a light source at the tip. The doctor can thus visualize the inner lining for any abnormality.
An individual undergoing flexible sigmoidoscopy has to undergo bowel preparation prior to the procedure. This is done so that the lower part of the colon is empty and the doctor can see the intestinal lining properly. Bowel preparation involves the use of enemas and/or oral laxatives.
During the sigmoidoscopy procedure, the patient is made to lie on his left side with his legs drawn to the chest. The doctor first inspects the anal opening for obvious lesions. He then inserts a gloved finger into the anus (this examination is called digital rectal examination) to check for any local obstruction. Following this examination, a lubricant is applied to the anal orifice and the tip of the sigmoidoscope is passed through the anus. The doctor examines the inner lining of the large intestines and rectum for any abnormality, especially as the scope is being withdrawn out. Air may also be introduced during the procedure for better visualization.
People opting for flexible sigmoidoscopy should repeat the test at least every 5 years.
1. Who should undergo flexible sigmoidoscopy?
A number of other screening tests such fecal occult blood testing and double contrast barium enema maybe used along with flexible sigmoidoscopy. Individuals who can have this screening procedure includes:
Patients who have undergone diversion of urine into this section of the colon. Individuals over the age of 50 years at average risk for developing colorectal cancer should undergo any of the tests on a regular basis.
2. How often should flexible sigmoidoscopy be repeated?
If all findings are normal, flexible sigmoidoscopy may be repeated every 5 years. People at high risk for developing colorectal cancer may have to undergo the test more often. These include:
- Individuals previously diagnosed with adenomatous polyps
- Individuals who have undergone surgery to remove prior colorectal cancer
- Individuals with immediate relatives diagnosed with precancerous colorectal polyps or colorectal cancer
- Individuals with inflammatory bowel disease like Crohn’s disease
- Individuals suffering from one out of two specific syndromes i.e. hereditary nonpolyposis colon cancer (HNPCC) or familial adenomatous polyposis
3. Who should not undergo flexible sigmoidoscopy?
Flexible sigmoidoscopy may not be possible in uncooperative people or people who are medically and emotionally unstable. Other conditions in which flexible sigmoidoscopy should be avoided include:
- Acute peritonitis (inflammation of the lining of the abdomen)
- Acute diverticulitis (inflammation of diverticula or small pouches in the intestines)
- Toxic megacolon (condition resulting in enlargement of bowel due to infection or inflammation)
- Recent bowel surgery
4. What are the advantages of flexible sigmoidoscopy?
Flexible sigmoidoscopy allows direct visualization of the lining of the last portion of the colon; thus it is a sensitive procedure to detect colorectal cancer in this portion. It is a quicker procedure than colonoscopy, usually lasting between 5 to 15 minutes. It does not require sedation and the person can return to work soon after the procedure.
5. What are the complications of flexible sigmoidoscopy?
Complications of flexible sigmoidoscopy include:
- Discomfort during the procedure
- Abdominal cramps and bloating following the procedure
- Bleeding following the procedure, which is usually minor
- Perforation of the bowel. This serious complication is usually rarely observed with the procedure
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Which doctor should I visit to get flexible sigmoidoscopy done?
You should visit a gastroenterologist to get a flexible sigmoidoscopy done. Sometimes, general practitioners may also do the procedure.
2. Is there anything called rigid sigmoidoscopy?
Rigid sigmoidoscopes are also available, but flexible sigmoidoscopes are preferred since they allow better visualization of the inner lining of the large intestine with minimal discomfort to the patient.
3. What is the difference between flexible sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy?
Flexible sigmoidoscopy is a faster procedure compared to colonoscopy. It does not require sedation and the person can return to work soon after the procedure. In contrast, colonoscopy takes longer time and requires sedation. However, colonoscopy permits examination of the entire colon whereas in sigmoidoscopy, only the last part of the colon is examined. Thus a number of cancers especially those on the right side could be missed in flexible sigmoidoscopy. Flexible sigmoidoscopy should be repeated every 5 years whereas colonoscopy every 10 years.
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA
 Email
Email