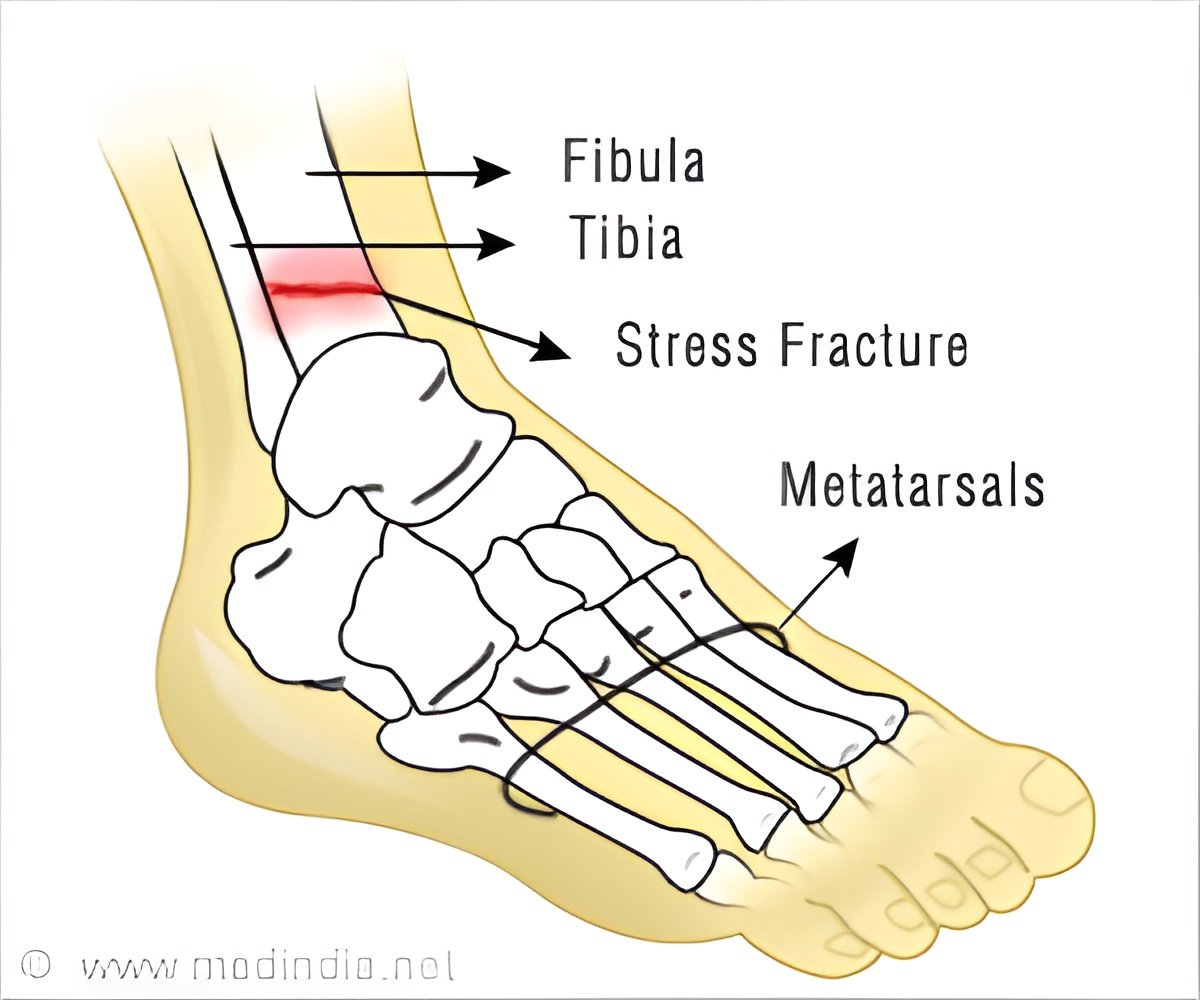
A stress fracture is a fatigue-induced fracture of the bone caused by repeated pressure over time such as running or jumping.
TOP INSIGHT
Two distinct variations within the purinergic receptor genes are associated with stress fracture injuries.
In this study, the researchers aimed to identify the contribution a specific gene had to stress fracture injuries in two groups of volunteers made up of military recruits and elite athletes.
The researchers evaluated the contribution the specific gene, P2X7R, had on the volunteers. The study was published in the journal Purinergic Signaling.
"The study found that two specific variations within the gene were associated with stress fracture injuries in healthy, exercising individuals," said one of the researchers Jim Gallagher from the University of Liverpool in England.
"The findings are the first to demonstrate an independent association between stress fracture injury and specific variations in purinergic receptor genes," Mr Gallagher noted.
"This work builds on pioneering basic laboratory research over several years in which we first showed that purinergic receptors are expressed in bone cells and that they regulate the response of bone to mechanical loading," Mr Gallagher pointed out.
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA


 Email
Email