Smoking has been linked to more rapid decline in the mental ability across all cognitive tests among men who smoked when compared to non-smoking men.
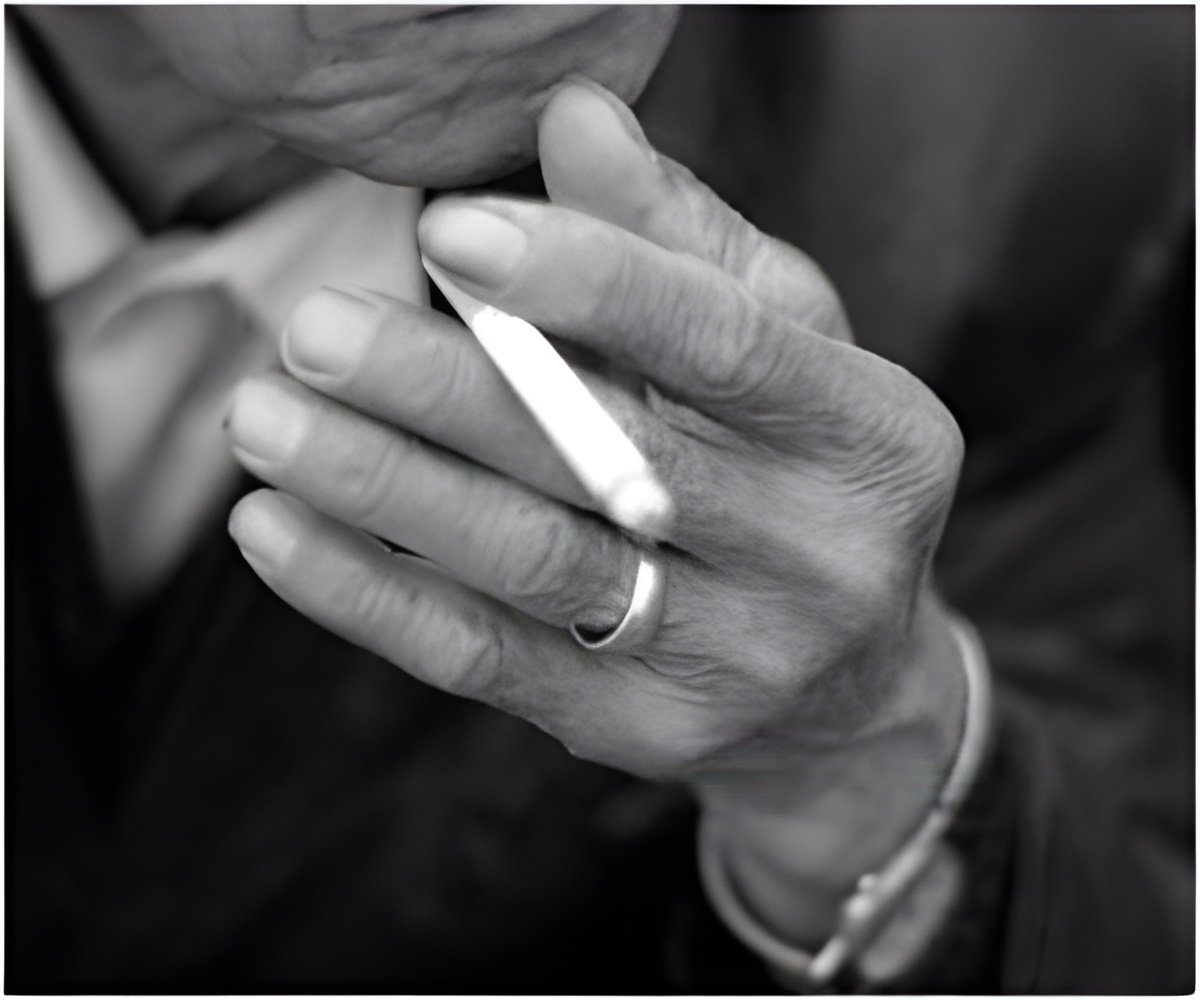

The exact reason for this sex-difference remains unclear. Researchers suggest that the higher volume and longer duration of cigarettes smoked by men in comparison to women could be the contributing factors. Other lifestyle habits, like drinking more alcohol, may also account for this difference.
The study lead Severine Sabia said, "Our results show that the association between smoking and cognition, particularly at older ages, is likely to be underestimated owing to higher risk of death and dropout among smokers."
The study illustrates the importance of examining risk factors for mental decline earlier in life.
The study is published in the Archives of General Psychiatry.
Source-Medindia
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA




 Email
Email