Scientists grew kidney-like structure using induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells, which is a complicated task as organs are composed of a multitude of different cell types.
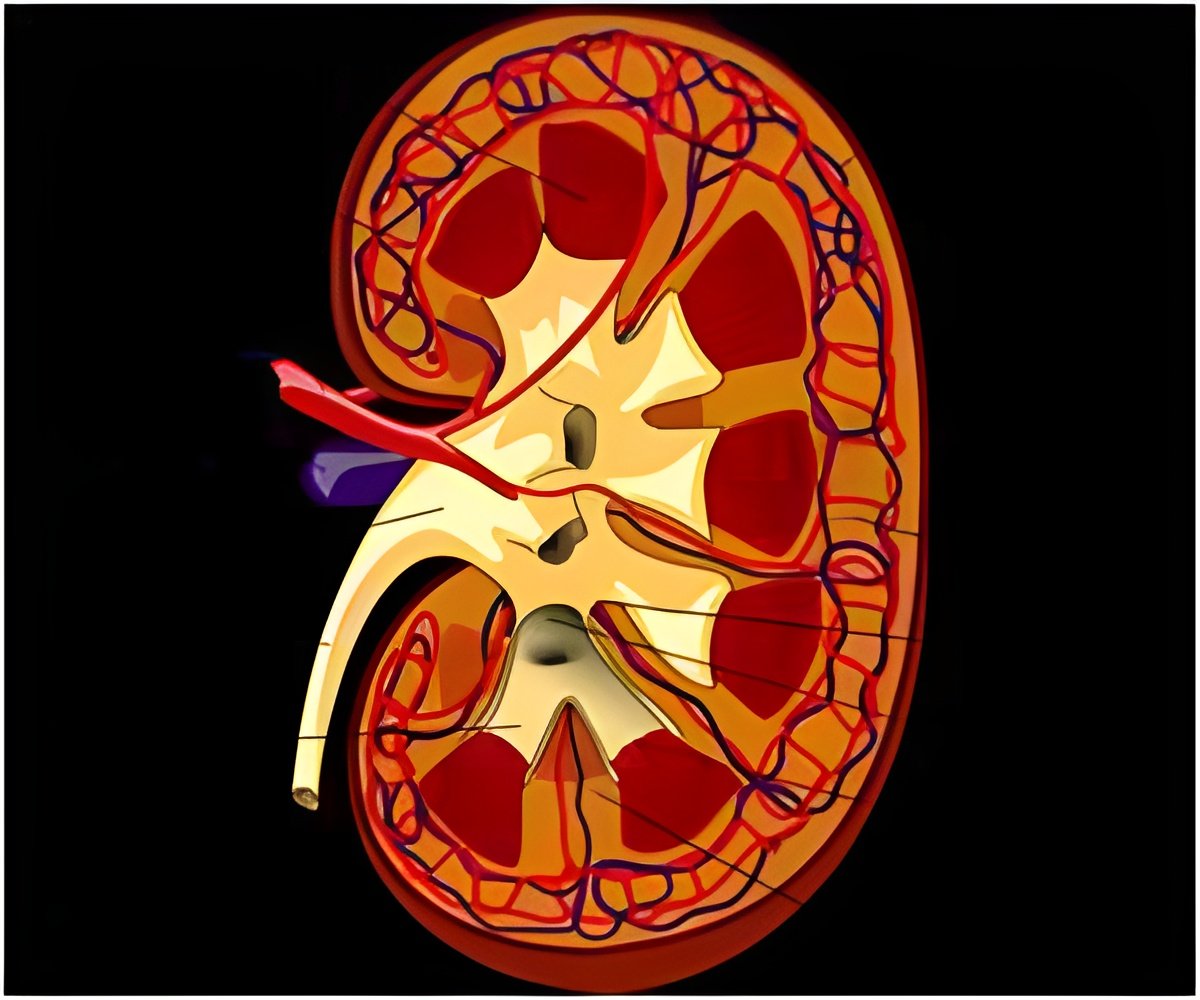
The researchers from Australia and the Netherlands grew their "kidney-like structure" from induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells -- adult cells reprogrammed into a neutral state from which they can be coaxed to develop into other cell types.
Given the critical shortage of donor organs to replace those damaged by accident or disease, it has long been a goal of science to create human organs from stem cells.
But it is a complicated task. Scientists need to prompt stem cells to become kidney, liver or lung cells, which must then recreate the complex anatomy of a real organ in order to function in a human recipient.
The first part of this chain has proved most challenging, especially in organs composed of a multitude of different cell types. The kidney, for example, has more than 20.
In the new study, published in the journal Nature, the team managed to transform iPS cells into two different adult cell types.
The resulting organoids sported different tissue types and were "similar" to the kidney of a human embryo, the researchers reported.
But he stressed the product was "not a kidney, but an organoid".
"There is a long way to go until clinically useful transplantable kidneys can be engineered," Davies said.
But the organoids may fulfil a completely different medical need -- testing the safety for humans of new drugs.
"The cell types that are most vulnerable to damage by drugs are present in the organoids," said Davies.
Stem cells are primitive cells that, as they grow, differentiate into the various specialized cells that make up the different organs -- the brain, the heart, the kidney, and so on.
Until a few years ago, when iPS cells were created, the only way to obtain stem cells was to harvest them from human embryos. This was controversial as it required the destruction of the embryo.
Other teams of scientists have also reported growing "organoid" stomachs, livers, retinas and brain and heart tissue from pluripotent stem cells in the lab.
Source-AFP
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA

 Email
Email










