A protein that encourages blood vessel growth especially 'bad' blood vessels has been identified by a team of scientists.
The study shows that, in mouse models, LRG1 promotes the growth of blood vessels in a process known as 'angiogenesis'. Conversely, inhibition of LRG1 in mouse models reduces the harmful blood vessel growth associated with retinal disease.
The authors of the study suggest that blocking LRG1's activity is a promising target for future therapy.
Professor John Greenwood, senior author of the research from the UCL Institute of Ophthalmology said: "We have discovered that a secreted protein, LRG1, promotes new blood vessel growth and its inhibition prevents pathological blood vessel growth in ocular disease."
"Our findings suggest that LRG1 has less of a role in normal blood vessel growth and so may be particularly applicable to 'bad' blood vessel growth. This makes LRG1 an especially attractive target for therapeutic intervention in conditions where vessel growth contributes to disease."
Angiogenesis is an essential biological process that is required for development, reproduction and the repair of damaged tissues. However angiogenesis also plays a major role in many diseases where new vessel growth can be harmful.
In previous studies, many signaling molecules have been identified that control angiogenesis, with the secreted protein vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) being considered as the master regulator. Therapeutic targeting of VEGF has resulted in improved outcomes in eye diseases with vascular complications and in some cancers but it is clear that additional therapeutic targets need to be identified.
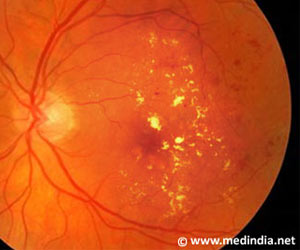
This study indicates that in the retinal diseases investigated LRG1 production is 'turned on' in blood vessels. This causes a switch in TGF-beta signalling away from a normal vessel maintenance pathway towards a pathway that promotes the growth of new harmful blood vessels.
Professor Stephen Moss, senior author from the UCL Institute of Ophthalmology said: "Genetic studies have revealed that the gene that codes for LRG1 is conserved in vertebrates, and this study confirms that mouse and human blood vessels express LRG1."
"We predict, therefore, that abnormal blood vessel growth is also a conserved process and that the role of LRG1 is equally applicable to human pathological angiogenesis."
He added: "Work is already underway to develop a therapeutic antibody that targets LRG1."
Source-Eurekalert
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA


 Email
Email










