A new technology emerging from The University of Nottingham in a study, is helping scientists to develop the first comprehensive model of a fully functioning fetal heart.
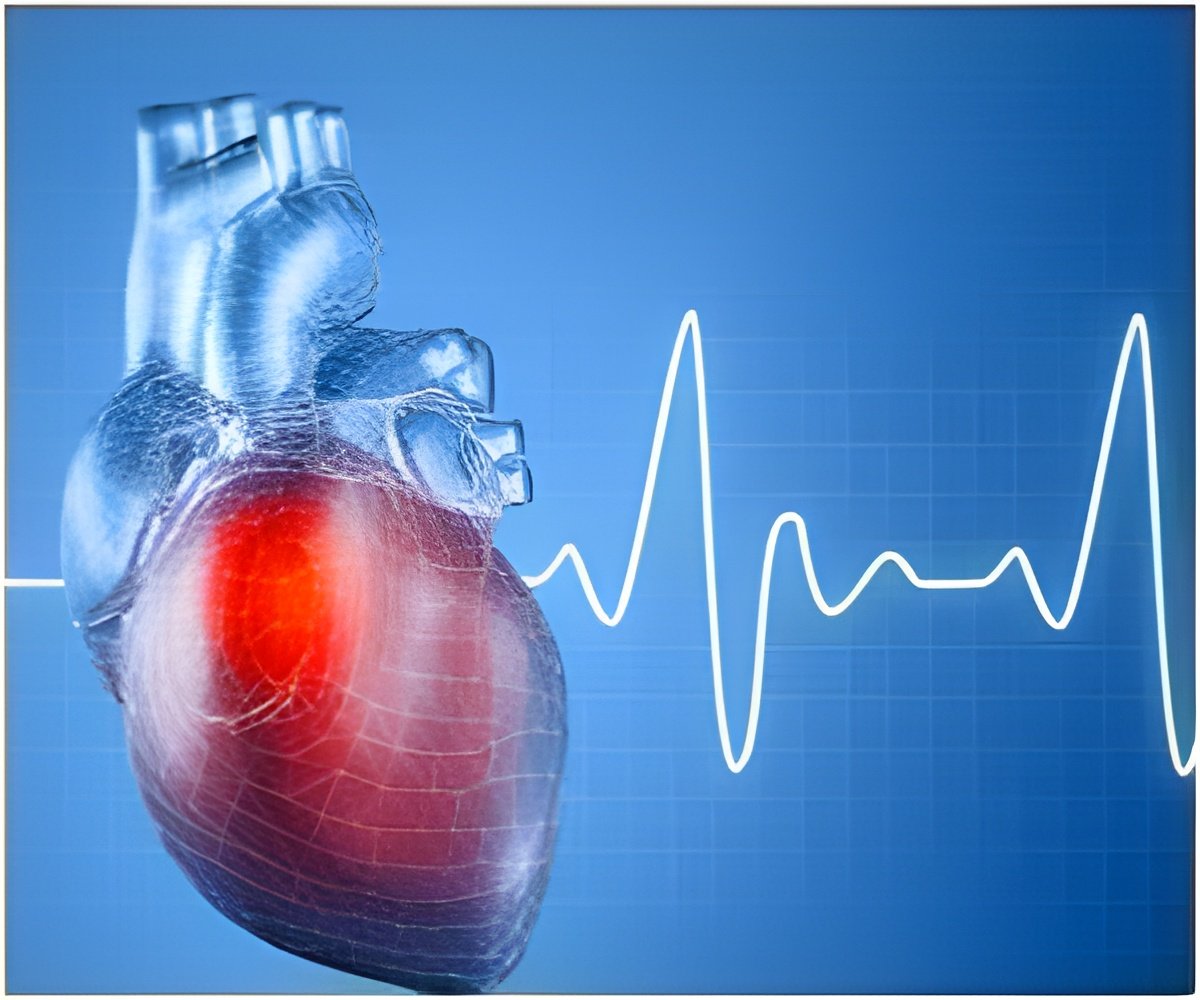
The collaborative study led by experts at The University of Leeds discovered that the walls of the human heart are a disorganised jumble of tissue until relatively late in pregnancy - with development much slower compared to other mammals.
Professor Barrie Hayes-Gill, Professor of Electronic Systems and Medical Devices at The University of Nottingham and joint founder and research director at Monica Healthcare said: "It's absolutely fantastic to see our device being used to detect fetal ECG morphology (i.e. ECG shape) in a non-invasive manner from the surface of the maternal abdomen."
"In this study the Monica device has been specifically deployed to observe the development of the fetal heart as it goes through gestation," he said.
The fetal heart monitor is a portable, non-invasive device which attaches to the mother's abdomen and measures the electrical activity from the heart of the baby inside her womb.
The device uses complex algorithms to correctly identify signals related to the fetal heart rate (FHR) using sensitive ECG-style electrodes. This method of using electrophysiological signals differs from current external monitoring devices that collect FHR and uterine activity data based on physical changes that may cause problems in data interpretation.
As part of their study, the team from the University of Leeds used the device to administer a weekly fetal ECG recording from 18 weeks until just before delivery.
Early results suggest that the human heart may develop on a different timeline from other mammals. While the tissue in the walls of a pig heart develops a highly organised structure at a relatively early stage of a fetus' development, their work suggests there is little organisation in the human heart's cells until 20 weeks into pregnancy.
The study has been published in the Journal of the Royal Society Interface Focus.
Source-ANI
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA


 Email
Email









