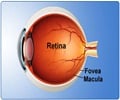
New research involving nearly one million patients shows that patients who were taking oral fluoroquinolones had a higher risk of developing a serious eye issue called retinal detachment

Mahyar Etminan, Pharm.D., M.Sc. (epi), of the Child and Family Research Institute of British Columbia, Vancouver, Canada, and colleagues conducted a study to examine the association between oral fluoroquinolone use and the risk of retinal detachment. The study consisted of a group of patients in British Columbia who had visited an ophthalmologist between January 2000 and December 2007. Retinal detachment cases were defined as a procedure code for retinal repair surgery within 14 days of a physician service code. Ten controls were selected for each case.
The overall cohort included 989,591 patients; within this group, 4,384 cases of retinal detachment and 43,840 corresponding controls were identified for analysis. Cases were more likely to be male and were more likely to have myopia (near-sightedness), diabetes, or have received cataract surgery. The researchers found that retinal detachment was associated with a higher likelihood of current use of fluoroquinolones (3.3 percent of cases vs. 0.6 percent of controls). For current users, the average number of days from the first fluoroquinolone prescription to the first event of a retinal detachment was 4.8 days. No risk was observed among recent users (0.3 percent of cases vs. 0.2 percent of controls) or past users (6.6 percent of cases vs. 6.1 percent of controls). The authors note that the absolute increase in the risk for this condition was small (number needed to harm = 2,500 for any use of fluoroquinolones).
No risk was observed among current users of β-lactam antibiotics or short-acting β-agonists.
"This is the first study, to our knowledge, demonstrating that oral fluoroquinolones are associated with an increase in the risk of a retinal detachment. Current users of oral fluoroquinolones were nearly 5 times more likely to be diagnosed with retinal detachment than nonusers," the researchers write, although because retinal detachment is rare among unexposed patients, the absolute risk increase is low.
The authors add that the risk of retinal detachment in their study was only elevated among current users but not among recent or past users, indicating an acute adverse event. They note that the exact mechanism of retinal detachment with fluoroquinolones is unknown.
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA


 Email
Email