From the University of Bonn and China, researchers have come across around 165 million years old fossil fly larva with an amazing sucking tool.
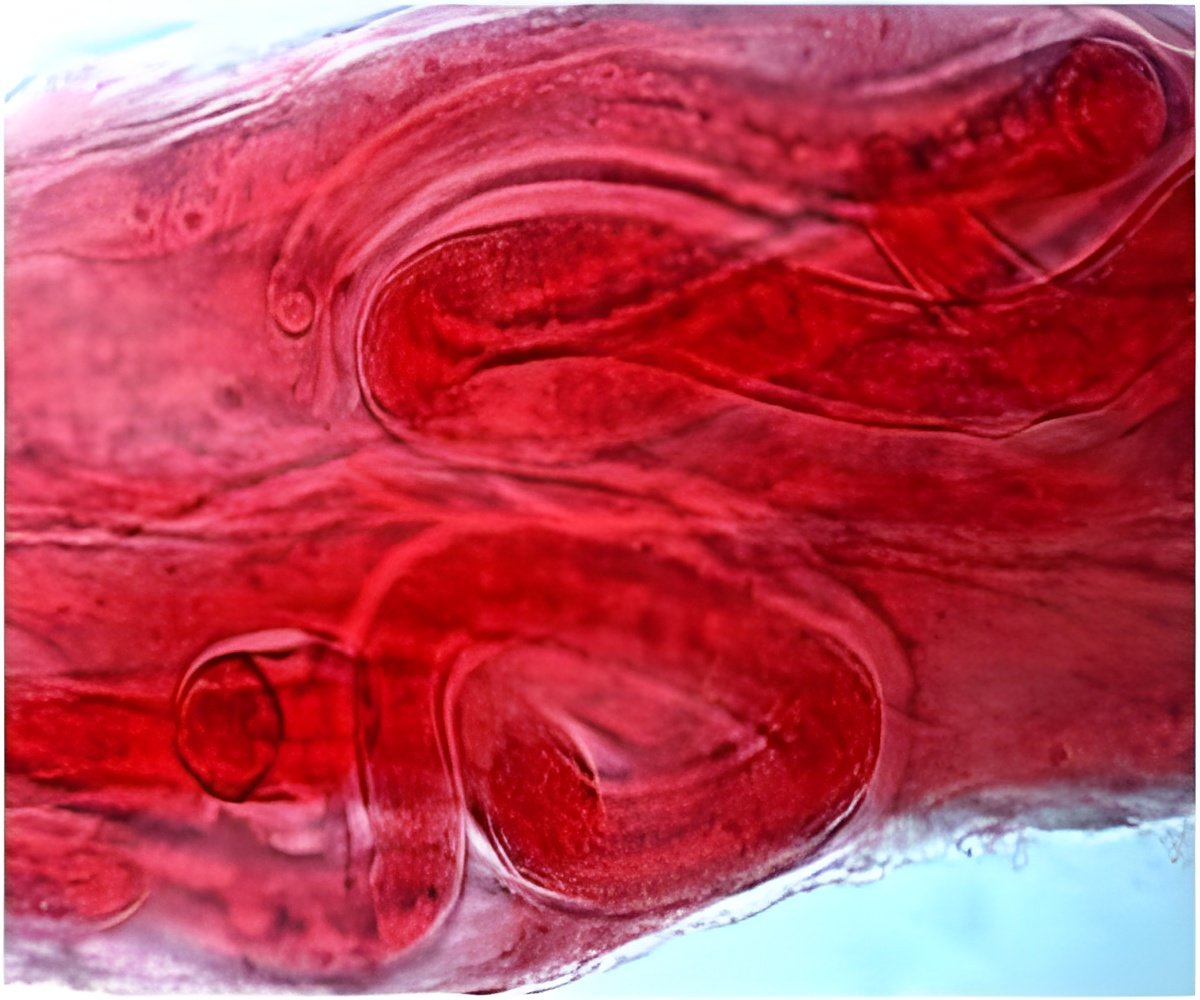
The international research team believes that this unusual animal is a parasite which lived in a landscape with volcanoes and lakes what is now northeastern China, and crawled onto passing salamanders, attached itself with its sucking plate, and penetrated the thin skin of the amphibians in order to suck blood from them.
Prof. Jes Rust the University of Bonn said that the parasite lived the life of Reilly, as there were many salamanders in the lakes, as fossil finds at the same location near Ningcheng in Inner Mongolia (China) have shown.
Dr. Bo Wang added that no insect exists today with a comparable body shape, and the bizarre larva from the Jurassic has remained so well-preserved to the present day was partly due to the fine-grained mudstone in which the animals were embedded.
The spectacular fly larva, has received the scientific name of 'Qiyia jurassica', as 'Qiyia' in Chinese means 'bizarre' while 'jurassica' refers to the Jurassic period to which the fossils belong.
For the international team of scientists from the University of Bonn, the Linyi University (China), the Nanjing Institute of Geology and Palaeontology (China), the University of Kansas (USA) and the Natural History Museum in London (England), the insect larva is a spectacular find.
The scientists don't yet have enough information to speculate as to what the adult it would have looked like, and how it might have lived.
Source-ANI
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA



 Email
Email






