The Legionnaires' disease was spread by a bacteria, which had been discovered in the cooling towers of 13 buildings in the South Bronx area, New York
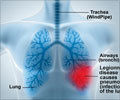
Legionnaires' disease is a serious pulmonary infection that is spread by bacteria that thrive in warm water, such as that found in hot water pipes, air-conditioning systems and industrial ponds. Infections result due to inhalation of airborne droplets of contaminated water. The incubation period of the disease lasts two to 10 days. An unprecedented outbreak of Legionnaires' disease in New York has seen 113 people contract this form of pneumonia, and the death toll has risen to 12.
76 people have now been treated and discharged from the hospital since the outbreak began on July 10, 2015, in the south Bronx, a less prosperous part of New York City. The disease was spread by a bacteria, which had been discovered in the cooling towers of 13 buildings in the South Bronx area. Mayor Bill de Blasio said, "The outbreak is tapering off. The illness is on the wane."
All the water bodies have since been cleaned and disinfected. Health officials have stressed that the dead were all older patients with pre-existing medical conditions.
Source-AFP