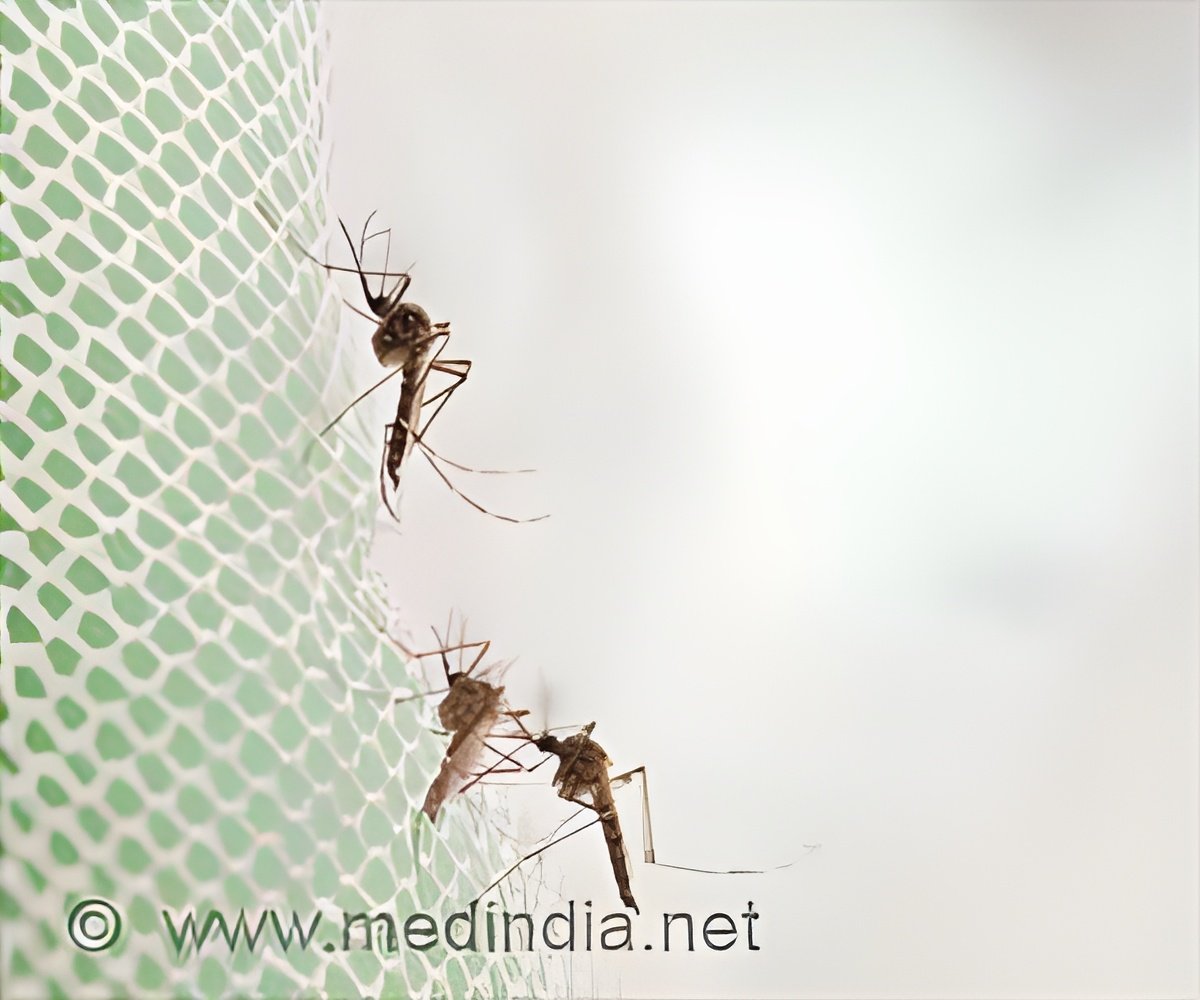
About 30 years ago, scientists identified a strain of bacteria that kills Anopheles. Since the bacteria's method of attack was not understood, it couldn't be replicated or used as an alternative to chemical insecticides -- until now.
An international team led by Sarjeet Gill, distinguished professor of molecular, cell and systems biology at UC Riverside, has identified a neurotoxin produced by the bacteria, and determined how it kills Anopheles. Their work is detailed in a paper published today in Nature Communications.
It took Gill and his team 10 years to achieve a breakthrough in their quest to understand the bacteria, and Gill attributes the success to modern gene sequencing techniques. They hit the bacteria with radiation, creating mutant bacterial strains that could not produce the toxin. By comparing the nontoxic strain to the one that kills Anopheles, they found proteins in the bacteria that are the keys to toxin production.
"Identifying the mechanisms by which the bacteria targets Anopheles has not been easy," Gill said. "We were excited not only to find the neurotoxin, called PMP1, but also several proteins that likely protect PMP1 as it's being absorbed in the mosquito's gut."
Many neurotoxins generally target vertebrates, and PMP1 bears 30 percent chemical similarity to botulinum or tetanus, both highly toxic to humans. Because the neurotoxin does not affect humans, vertebrates, fish, or even other insects, Gill believes the bacteria that produce PMP1 likely co-evolved along with Anopheles mosquitoes.
Advertisement
The team has applied for a patent on this discovery, and now hopes to find partners that will help them develop their bacteria-based Anopheles insecticide. These findings also open the door to new avenues of research on additional environmentally friendly insecticides.
Advertisement
Source-Eurekalert