Researchers have uncovered a crucial link between dietary zinc intake and protection against Streptococcus pneumoniae, the primary bacterial cause of pneumonia.
Dietary zinc was found to protect against Streptococcus pneumoniae infection, the primary bacterial cause of pneumonia, revealed new study.
Globally, it is estimated that nearly two billion people suffer from zinc deficiency, but why this increases susceptibility to bacterial infection has not been well understood - until now.
TOP INSIGHT
Zinc is mobilised to sites of infection where it stresses the invading bacteria and helps specific immune cells kill Streptococcus pneumoniae.
University of Melbourne Associate Professor Christopher McDevitt, a laboratory head at the Doherty Institute, led an interdisciplinary team using state-of-the-art imaging techniques to reveal how the immune system uses zinc as an antimicrobial for protection during attack by Streptococcus pneumoniae.
Published today in PLOS Pathogens, the team which included University of Adelaide Research Fellow Dr Bart Eijkelkamp, from the Research Centre for Infectious Diseases compared infections in mice fed with different levels of zinc.
They found that mice with lower zinc intake succumbed to infection up to three times faster because their immune systems had insufficient zinc to aid in killing the bacteria.
"Dietary zinc is associated with immune function and resistance to bacterial infection, but how it provides protection has remained elusive," Dr Eijkelkamp said.
This work also translated its findings by showing that specific human immune cells could use zinc to enhance their killing of invading Streptococcus pneumoniae.
"The findings in this paper are a direct result of application of novel elemental imaging technology to uncover relationships that have previously been hidden to analysis, and a testament to cross-disciplinary collaboration," said Professor Philip Doble, Director of the Elemental Bio-imaging Facility at the University of Technology Sydney, and a co-author of the study.
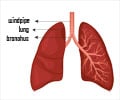
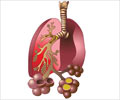
Pneumonia accounts for more than one million deaths every year, with the greatest health burden in countries where zinc deficiency frequently remains a major social challenge.
"Our findings highlight the importance of ensuring dietary zinc sufficiency as part of any population-wide strategy to control the burden of pneumococcal disease in conjunction with vaccination and other antimicrobial approaches," Associate Professor McDevitt said.'
Source-Eurekalert

 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA

 Email
Email