Researchers have puzzled over mechanisms that guide function and differentiation of blood stem cells for many years now.
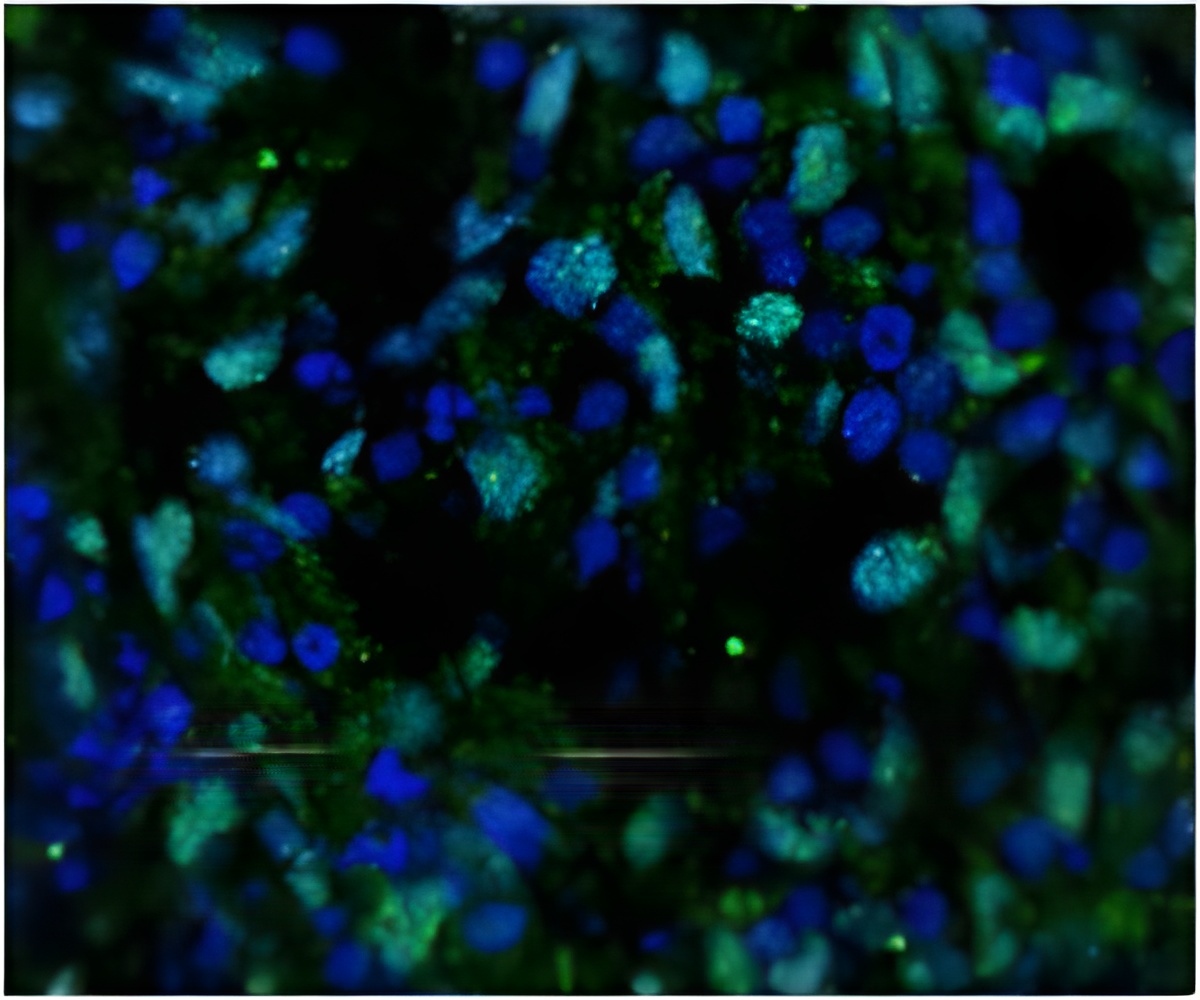
In the new model human blood stem cells can expand and differentiate into all cell types of the blood without any additional treatment. Even cells of the innate immune system that can normally not be found in "humanized" mice were efficiently generated in this mouse. Of significance is the fact that the stem cells can be maintained in the mouse over a longer period of time compared to previously existing mouse models. These results were now published in the renowned journal "Cell Stem Cell".
"Our goal was to develop an optimal model for the transplantation and study of human blood stem cells," says Claudia Waskow, who recently took office of the professorship for "animal models in hematopoiesis" at the medical faculty of the TU Dresden. Before, Prof. Waskow was a group leader at the DFG-Center for Regenerative Therapies Dresden where most of the study was conducted. The trick used by Claudia Waskow's team to achieve optimal stem cell engraftment was the introduction of a naturally occurring mutation of the Kit receptor into mice that lack a functional immune system. This way they circumvented the two major obstacles of blood stem cell transplantation: the rejection by the recipient's immune system and absence of free niche space for the incoming donor stem cells in the recipient's bone marrow. Space is usually provided by irradiation therapy, called conditioning, because it damages and depletes the endogenous stem cells and thus frees space for the incoming human cells. However, irradiation is toxic to many cell types and can lead to strong side effects. The Kit mutation in the new mouse model impairs the recipient's stem cell compartment in such a way that the endogenous blood stem cells can be easily replaced by human donor stem cells with a functional Kit receptor. This replacement works so efficiently that irradiation can be completely omitted allowing the study of human blood development in a physiological setting. The model can now be used to study diseases of the human blood and immune system or to test new treatment options. The results from Prof. Waskow's group also show that the Kit receptor is important for the function of human blood stem cells, notably in a transplantation setting. Further studies will now focus on using this knowledge about the role of the receptor to improve conditioning therapy in the setting of therapeutic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in patients.
Source-Eurekalert
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA

 Email
Email