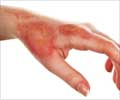
Indian scientists have created a skin gel made of silver nanoparticles that may help improve the treatment of burns and speed up healing.
Indian scientists have created a skin gel made of silver nanoparticles that may help improve the treatment of burns and speed up healing.
The researchers led by Kishore Paknikar have said that the new formula could be a potentially safer alternative to silver-based gels applied to the skin of burn patients to treat infections.With names like silver sulfadiazine and silver nitrate, these germ-fighters save lives and speed healing.
The researchers described that the gel is composed of silver nanoparticles - each 1/50,000th the width of a human hair - that appears more effective than these traditional gels.
They noted that antimicrobial silver compounds have been used for decades on burn patients, whose damaged skin is highly vulnerable to bacterial infections.
But, topical silver agents now in use can loose effectiveness in the body, cause skin discoloration, and damage cells. Drug-resistant bacteria can make these treatments less effective.
In the new research, the scientists demonstrated that their gel killed a broad range of harmful bacteria, including Pseudomonas aeruginosa-one of the most common causes of burn infections, as well as several drug-resistant microbes.
"These results clearly indicate that silver nanoparticles could provide a safer alternative to conventional antimicrobial agents in the form of a topical antimicrobial formulation," stated the article.
Source-ANI
SRM
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA



 Email
Email










