Assisted Reproductive Technology includes procedures in which egg and sperm are both handled, as in in-vitro fertilization.
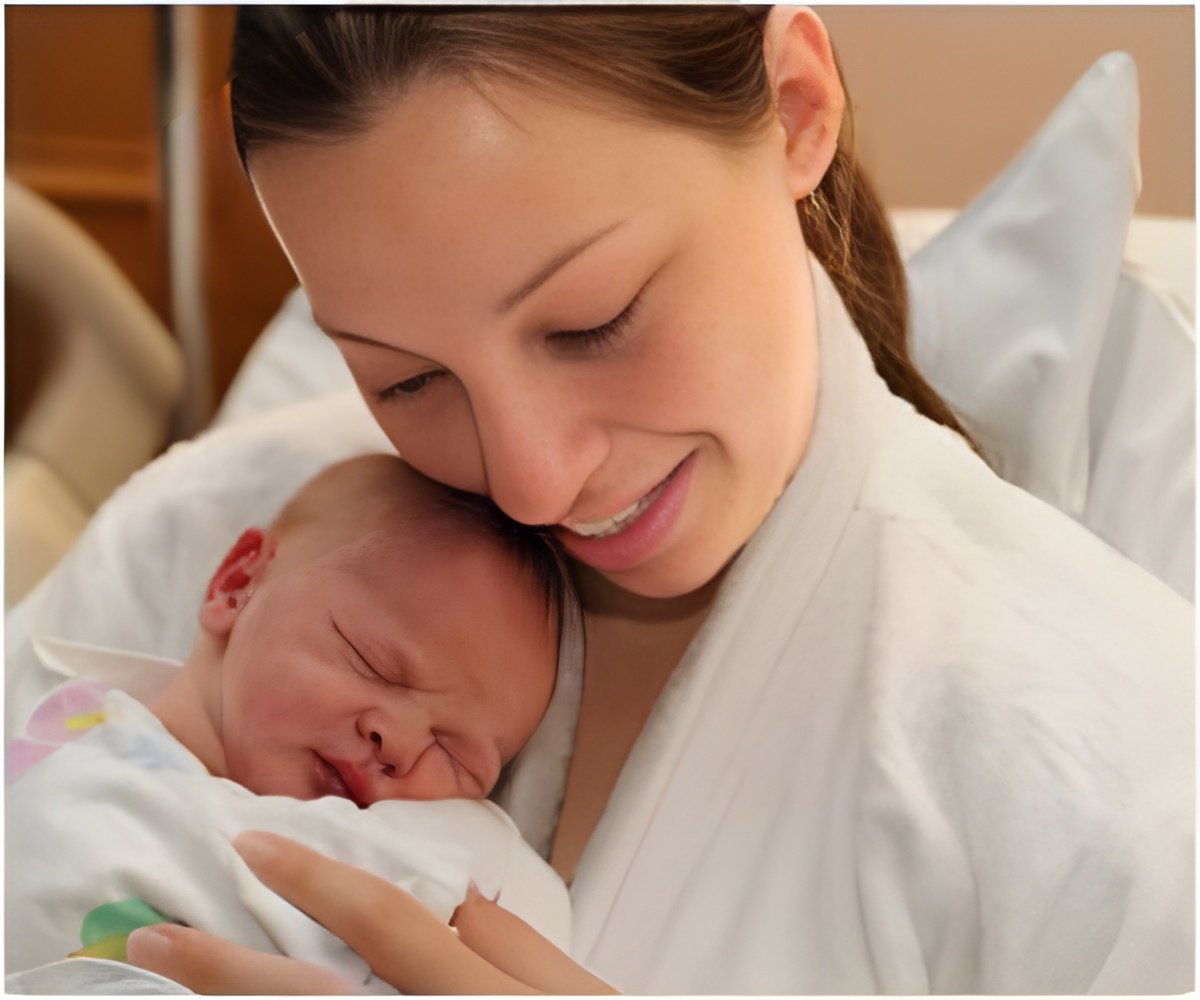

The study used data from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National ART Surveillance System between 2000 and 2011 and the database included more than one million ART cycles.
The researchers looked for complications from procedures to stimulate and extract eggs from the mother, and from implanting fresh embryos created from the mother’s own egg or from a donor.
"The results suggest that the treatment for Assisted Reproductive Technologyis relatively safe and that reported complications remain very rare. The results were not surprising and are very reassuring," said Dr. Jennifer F. Kawwass of Emory University School of Medicine in Atlanta.
The most common complication was ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS), essentially an overdose of those medications. It can cause ovaries to become swollen and painful, and in severe cases can involve rapid weight gain, vomiting and shortness of breath, according to the National Institutes of Health.
Bleeding, infections, severe OHSS, adverse reactions to other medications or anesthesia, hospitalization and maternal death all occurred in less than 10 of every 10,000 cycles. About 154 in every 10,000 cycles of ART using the mother’s own egg resulted in a report of OHSS.
Today, 1 percent of all infants born in the U.S. are conceived by ART. In 2012, 176,247 ART cycles were performed and resulted in 51,267 live births and 65,160 live born infants, according to the CDC.
The average cost of an in-vitro fertilization cycle in the U.S. is $12,400 (about 10,400 euros), according to the American Society for Reproductive Medicine.
Source-Medindia
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA


 Email
Email




