Newly developed model can assess the impact air pollution has on the development of childhood asthma.
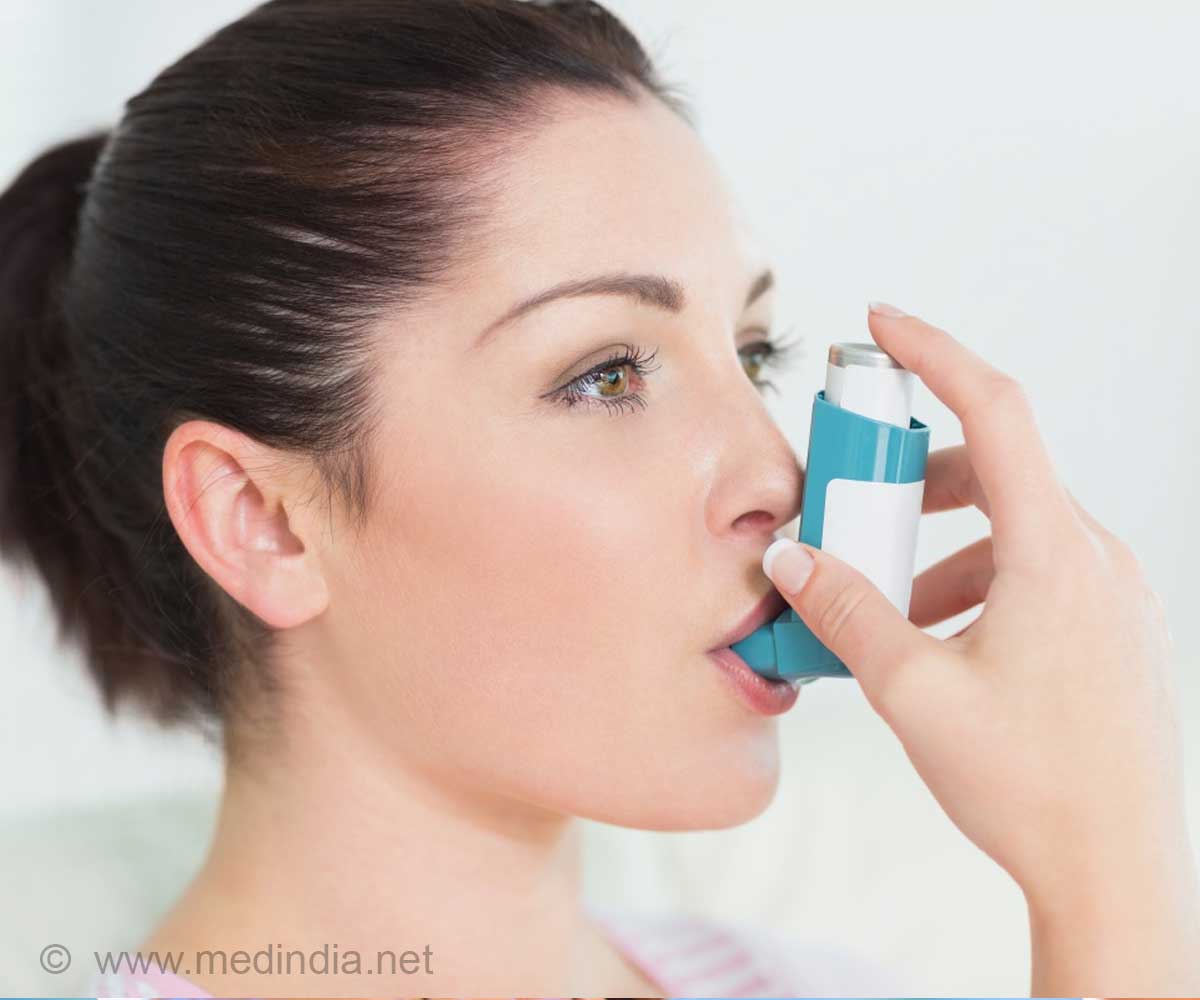

‘Up to 38% of all annual childhood asthma cases in Bradford may be attributable to air pollution and 12% of the cases would be attributable to traffic related air pollution specifically.’





The model knits together four distinct models of traffic, emissions, atmospheric dispersion and health impact assessments in Bradford. This allowed the researchers to chart the full chain of impact -- from the source of air pollution through the pathways in which it impacts children’s health. The results indicate that up to 38% of all annual childhood asthma cases in Bradford may be attributable to air pollution. More specifically, the model estimates showed that 12% of the annual childhood asthma cases would be attributable to traffic related air pollution.
"However, we knew our model was underestimating the traffic related fraction of air pollution. When we adjusted our results using actual measurements of air pollutants we saw that up to 24% of the annual cases could be attributable to traffic related air pollution," said study co-author, Professor Mark Nieuwenhuijsen, Director of the Urban Planning, Environment and Health Initiative at ISGlobal, a centre supported by The "la Caixa" Foundation.
Study lead author Dr Haneen Khreis carried out this research while at the Institute for Transport Studies at Leeds. She said: "Overall rates of childhood asthma cases in Bradford are higher than the national average as were emergency hospital admissions for asthmatic children under 16 years of age. Traffic-related air pollution is a real concern to the community.
"Our team’s previous research has shown that children exposed to high levels of traffic-related air pollution have a higher risk of developing asthma. Quantifying the number of childhood asthma cases that are directly attributable to traffic-related air pollution has not been done in the past and as we show now, a significant portion of cases is largely preventable."
Advertisement
"New policies aimed at reducing the effects of traffic-related air pollution need to target each link in the full chain of events -- from traffic volume and type, to exhaust and non-exhaust emissions, to dispersion to exposure."
Advertisement
Professor Nieuwenhuijsen said: "There is very little research that explores the impact of different exposure assessments. Cases of childhood asthma have been steadily increasing since the 1950s. Future progress with childhood asthma requires a focus beyond controlling and treating the disease toward asthma prevention starting with reducing traffic related air pollution."
The team’s research is part of ongoing work in Bradford assessing emissions and air quality profile in the region and the associated childhood health effects and impacts on the community.
Professor John Wright, Director of the Bradford Institute for Health Research and chief investigator of Born in Bradford, said: "This important study adds to the overwhelming evidence that air pollution is harming our children. The air in our cities has become a tragedy of the commons whereby a common good is being poisoned by collective neglect.
"The good news is that we can all save lives by driving less and using cleaner fuels."
Source-Eurekalert