Your emotional response to challenging situations could predict how your body responds to stress, new research has suggested.
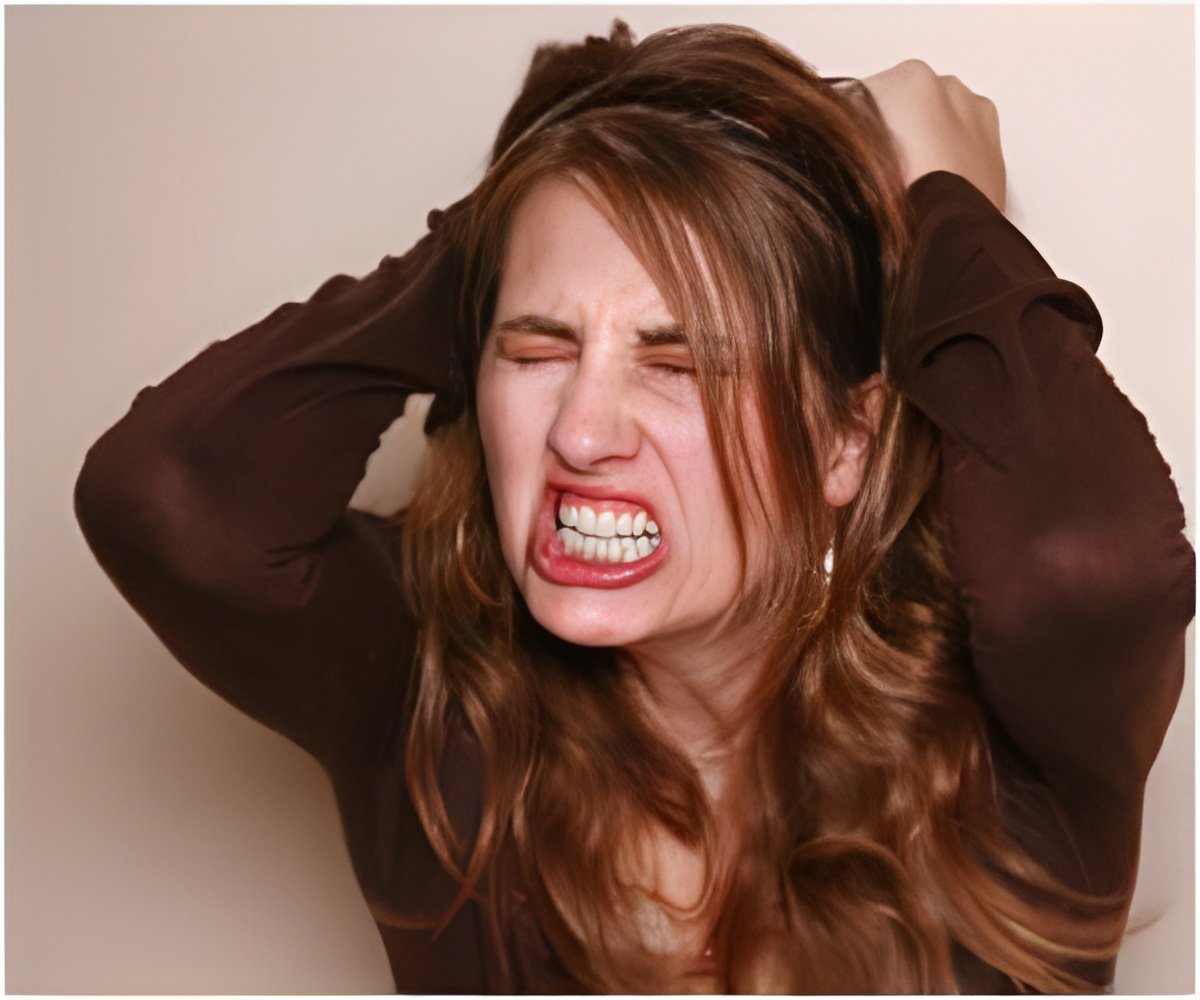

"This could help explain why some people with high levels of stress experience chronic health problems," she added.
The investigators asked healthy middle-aged individuals to complete a speech in the laboratory in front of video camera and a panel of judges. During the speech, they monitored the physical responses to the task and then afterwards asked them about the emotions that they had experienced.
"Most people show increases in heart rate and blood pressure when they complete a stressful task," explained Carroll, "but some also show increases in a circulating marker of inflammation known as interleukin-6. Our study shows that the people who have the biggest increases in this marker are the ones who show the greatest emotional responses to the task."
"Our results raise the possibility that individuals who become angry or anxious when confronting relatively minor challenges in their lives are prone to increases in inflammation," explained lead author Dr Anna Marsland, an Associate Professor of Psychology and Nursing at the University of Pittsburgh.
"Over time, this may render these emotionally-reactive individuals more vulnerable to inflammatory diseases, such as cardiovascular disease," she said.
Source-ANI
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA



 Email
Email