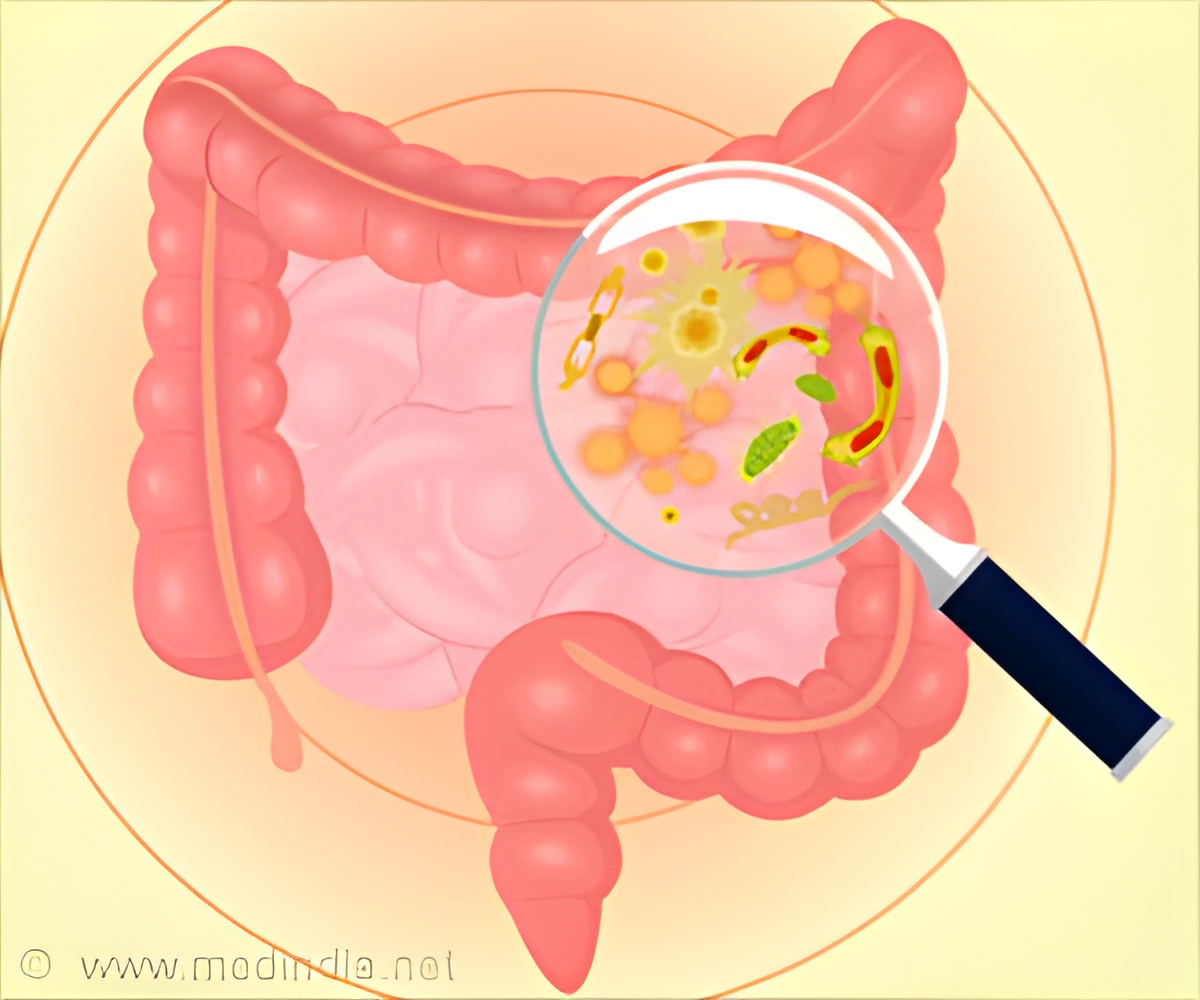
A small molecule called ‘PGE2’ activates specialized immune cells called as innate lymphoid cells to maintain a barrier between the gut and the body.
TOP INSIGHT
An immune system failure triggers the bacteria to escape from the gut and causes a massive inflammatory response, which can lead to multiple organ failures.
"Our study reveals a new approach that could be exploited as a treatment to help prevent one of the common causes of sepsis," Yao added.
The study, published in the journal Science, also helps explain why we do not suffer more infections, despite the vast number of bacteria that are found naturally in our gut.
Their escape is triggered by an immune system failure that causes a massive inflammatory response. This damages healthy tissues and can lead to multiple organ failures.
They found that a small molecule called "PGE2" plays a crucial role by activating specialized immune cells called innate lymphoid cells. These cells help to maintain the barrier between the gut and the rest of the body.
The findings could lead to new approaches for preventing whole-body infections which can be life-threatening if they are not caught early.
Source-IANS
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA



 Email
Email