Reducing obstructive sleep apnea using CPAP can reduce the need to get up and pee at night thereby improving the quality of life.

- Nocturia affects more than half of men and women over the age of 50 and is reported as the most irritating of all voiding symptoms.
- The prevalence of nocturia with among //patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea is 69%.
- Treatment with C-PAP, reduces nocturia in 65% of patients with 1 or more voiding episodes per night.
TOP INSIGHT
C-PAP has been suggested to decrease night-time urinary frequency, by reducing nocturnal urine production and improving patients' quality of life.
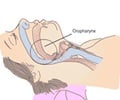
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSAS) affects between 2% and 4% of men and women over the age of 50. OSAS is caused by repetitive upper airway obstruction during sleep as a result of narrowing of the breathing passages. Obstruction is like strangulating a person repeatedly and depriving them of their constant oxygen supply to the body.
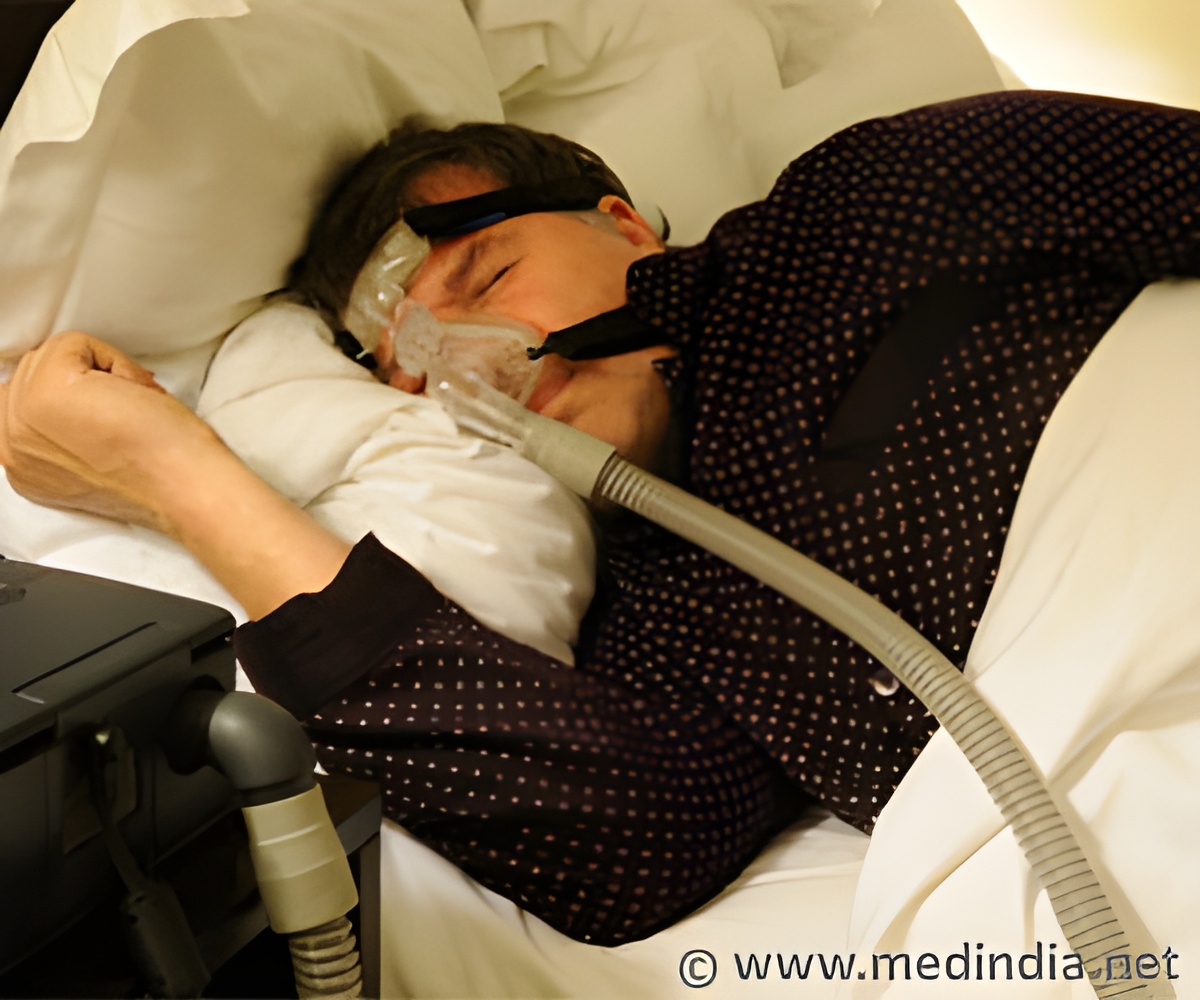
Patients are treated by wearing a special mask while asleep - a CPAP mask (Continuous Positive Airway Pressure mask), which increases the air pressure in the throat .
C-PAP Reduces Nocturia
Research, presented at the European Association of Urology conference in London, shows that wearing the mask reduces the frequency of nighttime peeing.
After starting to use the mask, nearly 2/3 of patients (65%) reported a reduction in the need to pee at night. The exact figure depended on the severity of the nocturia, with for example 32 of the 77 patients who previously reported 2 episodes per night, were able to pass the whole night undisturbed while to using the mask.
This study is the first large study to show a clear relationship between treatment with C-PAP in patients with primary OSAS complaints and the reduction of their nocturia episodes, stratified by the number of voiding episodes per night.
Reference
- Degalliers, S. et al., Reduction of nocturia in patients treated with C-PAP for obstructive sleep apnea syndrome, The 32nd European Association of Urology conference (2017).
Source-Medindia
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA



 Email
Email










