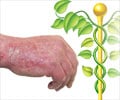
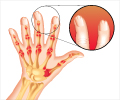
Combination of biologics with traditional therapy has been found to be beneficial in Psoriasis patients.
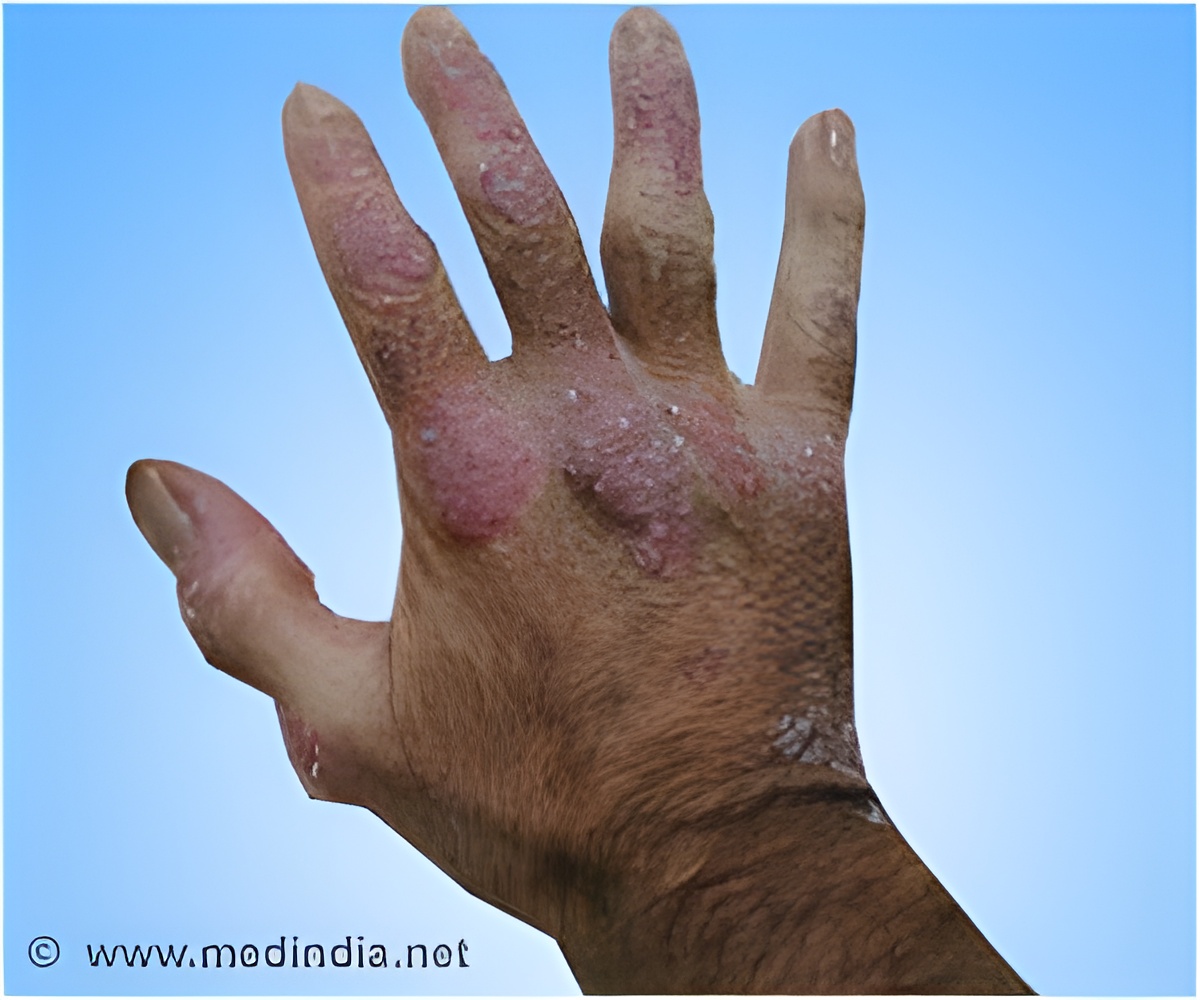
Moderate to severe psoriasis is treated with phototherapy, medications like methotrexate, acitretin, and cyclosporine, or biologics like adalimumab, alefacept, etanercept, infliximab, and ustekinumab. Biologics are medications isolated from a variety of natural sources like human, animal or microorganism and are produced by biotechnology methods and other technologies. In psoriasis, biologics act by inhibiting various steps in the inflammatory process that contribute to psoriasis.
Studies indicate that addition of a biologic to other medications used for psoriasis could help to reduce the dose of the medications and possibly discontinue them. Medications used in psoriasis have a number of side effects, thus reducing their dose could help to reduce their toxicity. In addition, biologics enhance the efficacy of traditional treatment. On the other hand, addition of the usual medications like local treatments, phototherapy or systemic medications to biologicals helps to increase the efficacy of the treatment. Combination of adalimumab with methotrexate; alefacept with topical or systemic agents; etanercept with calcipotriol, phototherapy, methotrexate, acitretin, or cyclosporine; and infliximab with methotrexate have been proved to be beneficial in various studies.
Thus, combination of the traditional treatments for psoriasis with biologics should be considered where treatment with a single agent is ineffective or the patient suffers from repeated flares.
Reference:
1. Guenther LC. Combination Therapy of Biologics with Traditional Agents in Psoriasis; Skin Therapy 2011.
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA


 Email
Email