The health minister of Democratic Republic of Congo has said that a fever of unidentified origin has killed 13 people in the northwestern area since August 11.
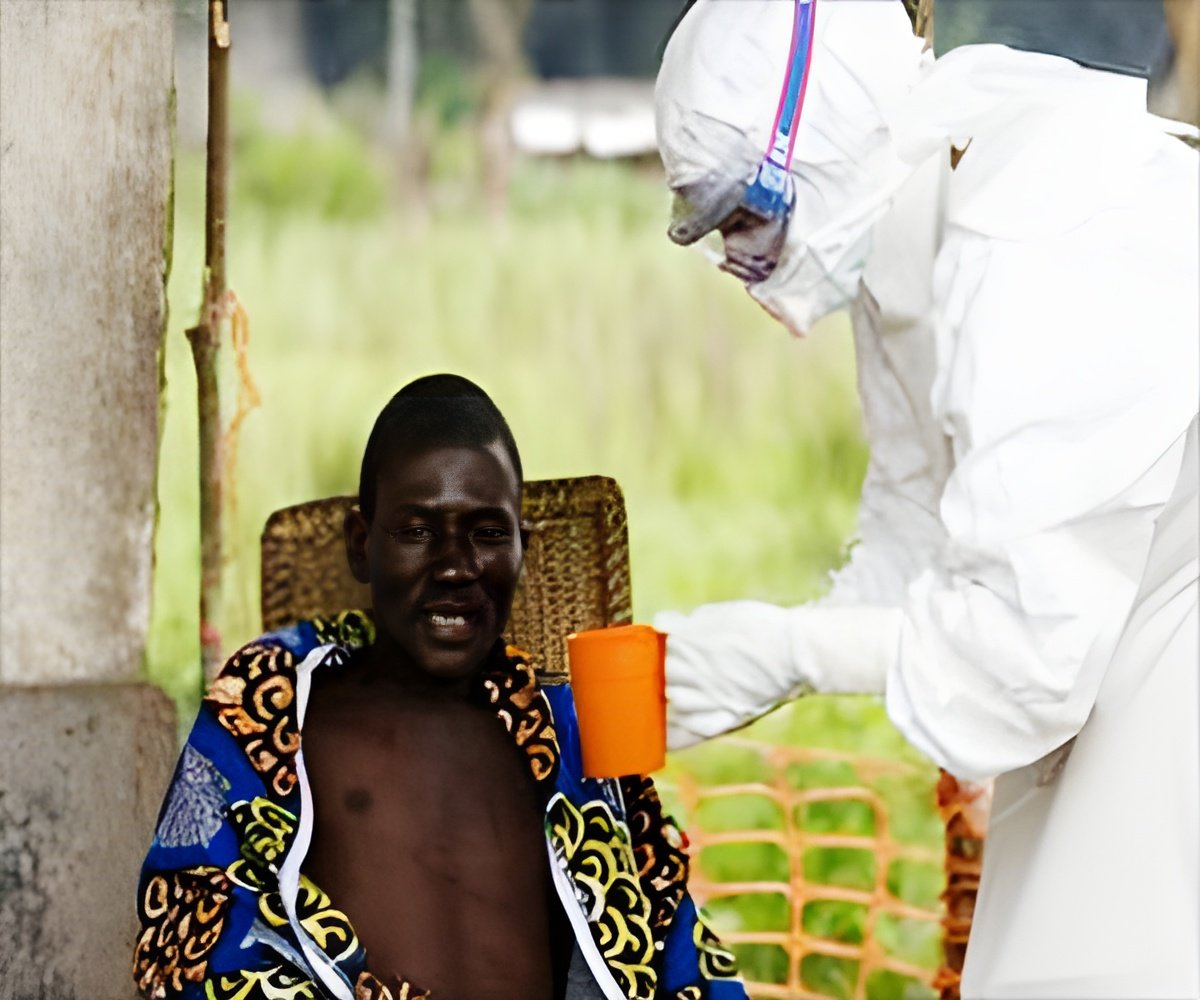
So far, about 80 people who came into contact with the deceased are being monitored at their homes, he added.
But a World Health Organization (WHO) official and the medical charity Doctors Without Borders (MSF) said Friday it was too soon to tell whether a haemorraghic fever caused the deaths, while an epidemic of often fatal and highly contagious Ebola raged in west Africa to the north.
"Many died presenting haemorragic symptoms, but there is also serious malaria that can cause this type of symptom, or typhoid fever," a WHO official based in Kinshasa told AFP, asking not to be named.
"We're still waiting for biological confirmation to find out what kind of disease this is," said Amandine Colin of MSF, which has teams in the affected territory of Boende, in Equateur province.
Samples have been taken to be examined at the National Institute of Biomedical Research as well as a specialised laboratory in Gabon, Numbi said, adding that the results should come within days.
Ebola was first identified in 1976 in Equateur in the former Zaire, today the DRC. The authorities have taken preventive health measures, including provisions for the safe burial of infected corpses and strict control of passengers arriving from affected countries.
Source-AFP
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA

 Email
Email