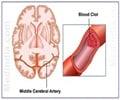
A new study has found that there is a higher risk of stroke and transient ischemic attack among older adults who have higher levels of stress, depression and hostility
Participants were 38.5 percent white, 27.8 percent African-American, 11.8 percent Chinese and 21.9 percent Hispanic. All were free of cardiovascular disease at the start of the study. In follow-up for an additional 8.5 to 11 years, 147 strokes and 48 TIAs occurred. Compared to people with the lowest psychological scores, those with highest scores were:
• 86 percent more likely to have a stroke or TIA for high depressive symptoms.
• 59 percent more likely to have a stroke or TIA for the highest chronic stress scores.
• More than twice as likely to have a stroke or TIA for the highest hostility scores.
• No significant increased risk was linked to anger.
"There's such a focus on traditional risk factors — cholesterol levels, blood pressure, smoking and so forth — and those are all very important, but studies like this one show that psychological characteristics are equally important," said Susan Everson-Rose, Ph.D., M.P.H., study lead author and associate professor of medicine at the University of Minnesota in Minneapolis.
These associations noted in the study were significant even when researchers accounted for age, race, sex, health behaviors and other known risk factors of stroke. "Given our aging population, it's important to consider these other factors that might play a role in disease risk. Stroke is a disease of the elderly predominantly, and so learning more about things that can influence risk for stroke as people age is important."
"One thing we didn't assess is coping strategies," Everson-Rose said. "If someone is experiencing depressive symptoms or feeling a lot of stress or hostility, we don't know how they manage those, so it's possible that positive coping strategies could ameliorate some of these associations or effects," she said. "We did not inquire about coping. I would say that's one of the tasks for future studies." Researchers didn't identify potential racial and ethnic differences or sex differences in the observed associations, but were not able to fully examine such differences due to the smaller numbers of strokes in some groups.
Source-Eurekalert
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA

 Email
Email










